Eriogonum visheri
Bot. Gaz. 56: 64. 1913.
Herbs, erect to spreading, annual, (1–)1.5–3.5(–4) dm, sparsely villous, grayish. Stems: caudex absent; aerial flowering stems erect, solid, not fistulose, 0.3–0.8(–1) dm, sparsely villous. Leaves basal and cauline; basal: petiole 1–3 cm, villous to pilose, blade elliptic to rotund, (0.8–)1–2.5 × (0.6–)1–2.5 cm, glabrous and green on both surfaces, margins entire, villous; cauline: petiole 0.5–1.5 cm, sparsely villous, blade elliptic, 0.5–1.5 × 0.5–1 cm, similar to basal blade. Inflorescences cymose, open, 5–35 × 5–35 cm; branches sparsely villous; bracts 3, scalelike, 1–2.5(–3) × 1–2.5 mm. Peduncles absent except in fork of proximal node, erect, straight, slender, 0.3–1(–1.5) cm, sparsely villous. Involucres turbinate, 1–1.5(–2) × 0.8–1.5 mm, glabrous; teeth 5, erect, 0.3–0.6(–0.8) mm. Flowers (1.2–)1.5–2.5 mm; perianth yellowish with darker yellow to greenish yellow or reddish brown midribs, sparsely hispid; tepals monomorphic, oblanceolate to oblong; stamens exserted, 1.2–1.7(–2) mm; filaments glabrous. Achenes shiny dark brown, 3-gonous, (2–)2.5–3 mm, glabrous.
Phenology: Flowering Jun–Aug.
Habitat: Loamy to clayey flats and outcrops, mixed grassland and saltbush communities
Elevation: 500-900 m
Distribution
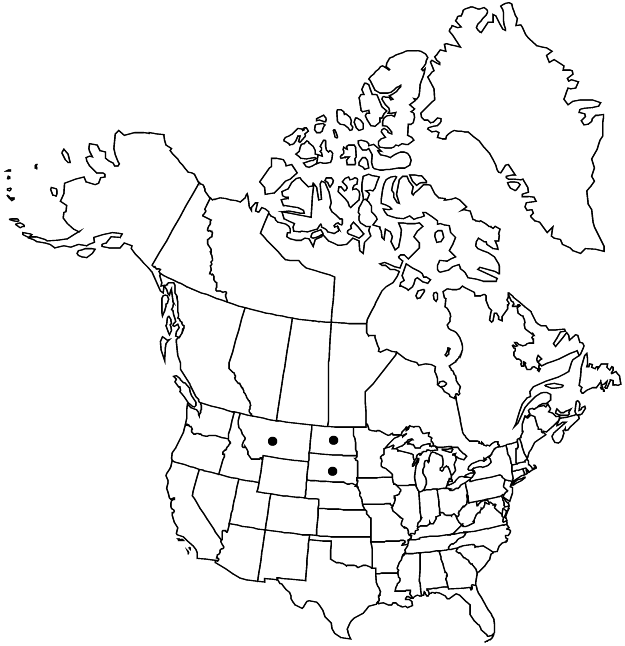
Mont., N.Dak., S.Dak.
Discussion
Eriogonum visheri is rare to infrequent throughout its range. It appears to be concentrated in two areas, one primarily in the “badlands” of western South Dakota and a second from the Cheyenne River northward to just north of the Cannonball River area in south-central North Dakota. It occurs also in Carter County, Montana. In South Dakota, the species is protected on the Buffalo Gap National Grassland, and is considered “sensitive” by the U.S. Forest Service. It is in the Center for Plant Conservation’s National Collection of Endangered Plants.
Selected References
None.