Potentilla crantzii
Excursionfl. Oesterreich 295. 1897.
Plants tufted to ± matted; caudex branches usually short, stout, sometimes elongate, slender. Stems ascending to erect, 0.5–2(–3) dm, lengths 1.5–3 times basal leaves. Basal leaves 2-ranked, usually palmate, sometimes ternate, 2–10(–15) cm; stipules: apex obtuse to truncate, rarely acute; petiole 0.5–6.5(–10) cm, long hairs usually ± sparse, usually ± ascending, sometimes spreading or appressed, 1–2.5 mm, weak to ± stiff, glands absent or sparse; leaflets 3–5, central obovate, 1.5–3(–3.5) × 0.8–1.5(–2) cm, petiolule 0–1 mm, margins flat, not lobed, distal 1/2–2/3 evenly incised 1/3–1/2 to midvein, teeth 3–4(–5) per side, not secondarily toothed, surfaces similar, green, not glaucous, hairs absent or sparse, rarely common, 0.8–1.5 mm, glands absent or sparse to abundant (fewer adaxially). Inflorescences (2–)3–8(–12)-flowered. Pedicels straight, 1–3(–4) cm in flower, to 6 cm in fruit. Flowers: epicalyx bractlets ovate or narrowly ovate, (1.5–)2.5–4 × (0.8–)1–1.3 mm, margins flat; hypanthium 3–4 mm diam.; sepals (3–)4–5(–6) mm, apex broadly acute; petals yellow, 4–7(–9) × 4–8 mm; filaments 1.8–2.2 mm, anthers 0.3–0.6 mm; carpels 30–40, styles columnar-filiform, not papillate-swollen proximally, 1–1.6 mm. Achenes 1.2 mm. 2n = 42; 28, 35, 49 (Europe).
Phenology: Flowering spring–summer.
Habitat: Herb meadows and slopes, usually on calcareous substrates, usually near coast
Elevation: 0–1700 m
Distribution
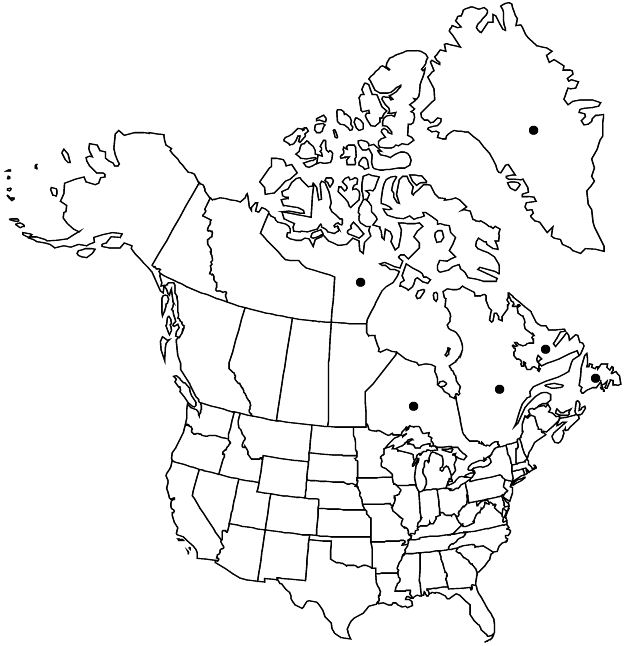
Greenland, Nfld. and Labr., Nunavut, Ont., Que., Eurasia, reportedly introduced in s Australia.
Discussion
Potentilla crantzii is primarily European, not restricted to coasts as in North America. The nomenclatural history is long and complex (A. Kurtto et al. in J. Jalas et al. 1972+, vol. 13), with P. alpestris and P. maculata in greatest historical use. The name P. ×protea Soják is available for presumed hybrids between P. crantzii and P. hyparctica.
The emphasis on two-ranked leaves to distinguish Potentilla crantzii from P. verna follows J. Soják (pers. comm.). Some collections of P. crantzii from Newfoundland approach P. verna in their more elongate caudex branches and shorter stature.
Selected References
None.