Difference between revisions of "Papaveraceae"
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Herbs </b>or subshrubs, shrubs, or small trees, annual, biennial, or perennial, scapose or caulescent, usually from taproots, sometimes from rhizomes; sap clear, white, or colored, often sticky. <b>Stems</b> leafy or naked, erect, spreading, or decumbent, simple or branching. <b>Leaves</b> basal and/or cauline, alternate to opposite or whorled, simple, without stipules, petiolate or sessile; blade unlobed or with 1-3 odd-pinnate, subpalmate, or palmate orders of lobes. <b>Inflorescences</b> axillary or terminal, unifloral or else multifloral and cymiform, racemose, umbelliform, corybiform, or paniculate, pedunculate or subsessile; bracts usually present. <b>Flowers</b> radially symmetric, pedicellate or sessile; receptacle sometimes expanded and forming cup or ring beneath calyx (only in Eschscholzia, Meconella, and Platystemon); perianth and androecium sometimes perigynous; sepals caducous, 2 or 3, distinct or connate, usually obovate; petals distinct, usually obovate, mostly 2 times number of sepals, sometimes more or absent; stamens many or 4-15 (only in Meconella and Canbya); anthers 2-locular; pistil 1, 2-18[-22]-carpellate; ovary 1-2-locular or incompletely to completely multilocular by placental intrusion; placentas 2 or more, parietal; style 1 or absent; stigmas or stigma lobes 2-many. <b>Fruits</b> capsular, dehiscence valvate, poricidal, or transverse, or carpels dissociating and breaking transversely into 1-seeded segments (only in Platystemon). <b>Seeds</b> usually many, small, sometimes arillate or carunculate.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| − | |distribution=Worldwide;mainly Northern Hemisphere | + | |distribution=Worldwide;mainly Northern Hemisphere. |
|discussion=<p>Genera 25-30 (17 genera, 63 species in the flora).</p><!-- | |discussion=<p>Genera 25-30 (17 genera, 63 species in the flora).</p><!-- | ||
--><p>According to W. R. Ernst (1962b), Papaveraceae "may be divided conveniently into four subfamilies." His scheme is followed here, but with the subfamilies taken up in alphabetic order; they seem to be natural groups, but their phylogenetic interrelationships are not yet clear. Similarly, the evolutionary relationships within the subfamilies remain ambiguous, and the genera in each are listed alphabetically. Subfamily Chelidonioideae Ernst includes genera 1-5; subf. Eschscholzioideae Ernst, genera 6-7; subf. Papavaroideae Ernst, genera 8-14; and subf. Platostamenoideae Ernst, genera 15-17.</p><!-- | --><p>According to W. R. Ernst (1962b), Papaveraceae "may be divided conveniently into four subfamilies." His scheme is followed here, but with the subfamilies taken up in alphabetic order; they seem to be natural groups, but their phylogenetic interrelationships are not yet clear. Similarly, the evolutionary relationships within the subfamilies remain ambiguous, and the genera in each are listed alphabetically. Subfamily Chelidonioideae Ernst includes genera 1-5; subf. Eschscholzioideae Ernst, genera 6-7; subf. Papavaroideae Ernst, genera 8-14; and subf. Platostamenoideae Ernst, genera 15-17.</p><!-- | ||
| Line 221: | Line 221: | ||
|family=Papaveraceae | |family=Papaveraceae | ||
|illustrator=John Myers | |illustrator=John Myers | ||
| − | |distribution=Worldwide;mainly Northern Hemisphere | + | |distribution=Worldwide;mainly Northern Hemisphere. |
|reference=ernst1962b;ernst1962c;ernst1967a;fedde1909a;fedde1936a;gunn1976a;gunn1980b;harms1936a;hutchinson1925a;kadereit1993a;stermitz1968a;wilson1993a | |reference=ernst1962b;ernst1962c;ernst1967a;fedde1909a;fedde1936a;gunn1976a;gunn1980b;harms1936a;hutchinson1925a;kadereit1993a;stermitz1968a;wilson1993a | ||
|publication title= | |publication title= | ||
|publication year= | |publication year= | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna- | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/9216fc802291cd3df363fd52122300479582ede7/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V3/V3_240.xml |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]] | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 27 July 2019
Herbs or subshrubs, shrubs, or small trees, annual, biennial, or perennial, scapose or caulescent, usually from taproots, sometimes from rhizomes; sap clear, white, or colored, often sticky. Stems leafy or naked, erect, spreading, or decumbent, simple or branching. Leaves basal and/or cauline, alternate to opposite or whorled, simple, without stipules, petiolate or sessile; blade unlobed or with 1-3 odd-pinnate, subpalmate, or palmate orders of lobes. Inflorescences axillary or terminal, unifloral or else multifloral and cymiform, racemose, umbelliform, corybiform, or paniculate, pedunculate or subsessile; bracts usually present. Flowers radially symmetric, pedicellate or sessile; receptacle sometimes expanded and forming cup or ring beneath calyx (only in Eschscholzia, Meconella, and Platystemon); perianth and androecium sometimes perigynous; sepals caducous, 2 or 3, distinct or connate, usually obovate; petals distinct, usually obovate, mostly 2 times number of sepals, sometimes more or absent; stamens many or 4-15 (only in Meconella and Canbya); anthers 2-locular; pistil 1, 2-18[-22]-carpellate; ovary 1-2-locular or incompletely to completely multilocular by placental intrusion; placentas 2 or more, parietal; style 1 or absent; stigmas or stigma lobes 2-many. Fruits capsular, dehiscence valvate, poricidal, or transverse, or carpels dissociating and breaking transversely into 1-seeded segments (only in Platystemon). Seeds usually many, small, sometimes arillate or carunculate.
Distribution
Worldwide, mainly Northern Hemisphere.
Discussion
Genera 25-30 (17 genera, 63 species in the flora).
According to W. R. Ernst (1962b), Papaveraceae "may be divided conveniently into four subfamilies." His scheme is followed here, but with the subfamilies taken up in alphabetic order; they seem to be natural groups, but their phylogenetic interrelationships are not yet clear. Similarly, the evolutionary relationships within the subfamilies remain ambiguous, and the genera in each are listed alphabetically. Subfamily Chelidonioideae Ernst includes genera 1-5; subf. Eschscholzioideae Ernst, genera 6-7; subf. Papavaroideae Ernst, genera 8-14; and subf. Platostamenoideae Ernst, genera 15-17.
Hunnemannia fumariifolia Sweet, native to the highlands of Mexico, is occasionally found in California as a garden escape. A glabrous perennial with glaucous, blue-gray stem and leaves, and glossy, yellow petals, it bears an overall resemblance to Eschscholzia but has distinct sepals, no receptacular cup, and a peltate stigma. Below, it would key out as Arctomecon.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Illustrations
Key
| 1 | Leaves opposite or whorled. | > 2 |
| 1 | Leaves alternate or subopposite (sometimes only 1 in Sanguinaria). | > 4 |
| 2 | Plants glabrous or glabrate; blades of proximal leaves linear-spatulate; stamens 4-12; capsules linear. | Meconella |
| 2 | Plants usually distinctly pubescent; blades of proximal leaves broadly linear; stamens 12 or more; capsules not linear. | > 3 |
| 3 | Stems branching distally; stigmas and carpels 6 or more, carpels dissociating and breaking transversely into 1-seeded segments. | Platystemon |
| 3 | Stems branching from base; stigmas and carpels 3, carpels not dissociating, not breaking into transverse segments, capsules valvate. | Hesperomecon |
| 4 | Plants subshrubby or shrubby. | > 5 |
| 4 | Plants herbaceous. | > 7 |
| 5 | Leaf blades and capsules harshly prickly. | Argemone |
| 5 | Leaf blades and capsules not harshly prickly, sometimes bristly. | > 6 |
| 6 | Leaf blades lobed; petals white. | Romneya |
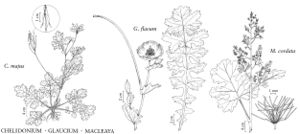
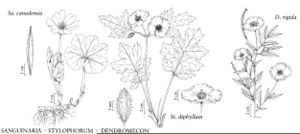
| 6 | Leaf blades unlobed; petals yellow. | Dendromecon |
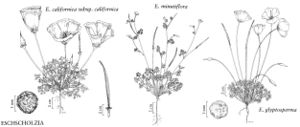
| 7 | Sepals connate, calyptrate; evident receptacular cup beneath calyx. | Eschscholzia |
| 7 | Sepals distinct, not calyptrate; receptacular cup absent or obscure. | > 8 |
| 8 | Inflorescences paniculate; petals absent. | Macleaya |
| 8 | Inflorescences not paniculate; petals present. | > 9 |
| 9 | Inflorescences umbelliform. | > 10 |
| 9 | Inflorescences not umbelliform. | > 11 |
| 10 | Stigma lobes 2; capsule 2-valved, dehiscing from base, glabrous. | Chelidonium |
| 10 | Stigma lobes 3-4(-5); capsule (3-)4-valved, dehiscing from apex, pubescent. | Stylophorum |
| 11 | Leaf blades and capsules harshly prickly. | Argemone |
| 11 | Leaf blades and capsules not harshly prickly. | > 12 |
| 12 | Stigmas radiating on sessile disc. | Papaver |
| 12 | Stigmatic disc absent. | > 13 |
| 13 | Style absent or indistinct. | > 14 |
| 13 | Style present. | > 17 |
| 14 | Sap clear; leaf blades unlobed or lobed only distally; petals 5-7. | > 15 |
| 14 | Sap yellow; leaf blades lobed throughout; petals 4. | > 16 |
| 15 | Leaf blades glabrous; inflorescences 1-flowered; stamens 6-15. | Canbya |
| 15 | Leaf blades long-pilose; inflorescences 3-20-flowered; stamens many. | Arctomecon |
| 16 | Petals yellow to reddish orange; filaments yellow. | Glaucium |
| 16 | Petals bright red; filaments dark violet or black. | Roemeria |
| 17 | Leaf blades palmately lobed throughout. | Sanguinaria |
| 17 | Leaf blades pinnately lobed throughout or lobed only distally. | > 18 |
| 18 | Leaf blades pinnately lobed throughout; petals orange-red, spotted purple at base, caducous. | Stylomecon |
| 18 | Leaf blades lobed only distally; petals white or yellow, unspotted, persistent. | Arctomecon |