Difference between revisions of "Drymocallis glandulosa"
Monogr. N. Amer. Potentilleae, 198. 1898.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Caudex </b>branches short. <b>Stems</b> tufted, (1–)1.5–7.5 dm; base 1–5 mm diam., moderately to densely septate-glandular. <b>Leaves</b> sparsely to moderately hairy; basal (3–)6–30 cm, leaflet pairs (1–)2–4; terminal leaflet broadly obovate to rhombic-elliptic, (1–)1.5–7(–8) × 1–5 cm, teeth usually double (irregularly single in var. viscida), (4–)6–18(–20) per side, apex rounded to obtuse; cauline 0–3, developed or reduced, leaflet pairs 1–4. <b>Inflorescences</b> (2–)5–40-flowered, leafy or not, open or of congested clusters terminating branches, (1/10–)1/5–3/4 of stem, usually wide (narrow in var. viscida), branch angles (15–)20–55°. <b>Pedicels</b> 1–10 (proximal to 30) mm, not or sparsely short-hairy, predominantly septate-glandular. <b>Flowers</b> opening widely; epicalyx bractlets linear-lanceolate to elliptic, 1.5–7(–8) × 0.5–2.5(–3) mm; sepals spreading or reflexed, (3–)4–11 mm, apex usually broadly obtuse with mucronate tip, sometimes acute; petals not overlapping, spreading or reflexed, cream-white to yellow, narrowly to broadly obovate or ovate to nearly round, 2–6.5 × 1.5–5.5 mm, shorter than or equal to sepals; filaments 0.5–2 mm, anthers 0.5–1 mm; styles thickened, 1–1.5 mm. <b>Achenes</b> reddish brown, 0.9–1.5 mm.</span><!-- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Caudex </b>branches short. <b>Stems</b> tufted, (1–)1.5–7.5 dm; base 1–5 mm diam., moderately to densely septate-glandular. <b>Leaves</b> sparsely to moderately hairy; basal (3–)6–30 cm, leaflet pairs (1–)2–4; terminal leaflet broadly obovate to rhombic-elliptic, (1–)1.5–7(–8) × 1–5 cm, teeth usually double (irregularly single in <i></i>var.<i> viscida</i>), (4–)6–18(–20) per side, apex rounded to obtuse; cauline 0–3, developed or reduced, leaflet pairs 1–4. <b>Inflorescences</b> (2–)5–40-flowered, leafy or not, open or of congested clusters terminating branches, (1/10–)1/5–3/4 of stem, usually wide (narrow in <i></i>var.<i> viscida</i>), branch angles (15–)20–55°. <b>Pedicels</b> 1–10 (proximal to 30) mm, not or sparsely short-hairy, predominantly septate-glandular. <b>Flowers</b> opening widely; epicalyx bractlets linear-lanceolate to elliptic, 1.5–7(–8) × 0.5–2.5(–3) mm; sepals spreading or reflexed, (3–)4–11 mm, apex usually broadly obtuse with mucronate tip, sometimes acute; petals not overlapping, spreading or reflexed, cream-white to yellow, narrowly to broadly obovate or ovate to nearly round, 2–6.5 × 1.5–5.5 mm, shorter than or equal to sepals; filaments 0.5–2 mm, anthers 0.5–1 mm; styles thickened, 1–1.5 mm. <b>Achenes</b> reddish brown, 0.9–1.5 mm.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
|distribution=w North America;nw Mexico. | |distribution=w North America;nw Mexico. | ||
|discussion=<p>Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).</p><!-- | |discussion=<p>Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).</p><!-- | ||
| − | --><p>Even with the removal of most of the subspecies of Potentilla glandulosa treated by Keck, Drymocallis glandulosa encompasses an inordinate range of variation. This is because of the apparently clinal variation between the coastal extreme (var. wrangelliana), with leafy inflorescences and broad cream-white petals, the montane var. reflexa, with less leafy inflorescences and narrow yellow petals, and the transitional interior var. glandulosa. Variety reflexa, in turn, intergrades in the mountains of southern California with var. viscida, which is anomalous in D. glandulosa with its narrow inflorescences and irregularly single-toothed leaflets. Variation outside of California is unclear, with no evident pattern to differences in petal size and color; these have largely been assigned to var. glandulosa.</p><!-- | + | --><p>Even with the removal of most of the subspecies of <i>Potentilla</i> glandulosa treated by Keck, <i>Drymocallis glandulosa</i> encompasses an inordinate range of variation. This is because of the apparently clinal variation between the coastal extreme (<i></i>var.<i> wrangelliana</i>), with leafy inflorescences and broad cream-white petals, the montane <i></i>var.<i> reflexa</i>, with less leafy inflorescences and narrow yellow petals, and the transitional interior <i></i>var.<i> glandulosa</i>. Variety reflexa, in turn, intergrades in the mountains of southern California with <i></i>var.<i> viscida</i>, which is anomalous in <i>D. glandulosa</i> with its narrow inflorescences and irregularly single-toothed leaflets. Variation outside of California is unclear, with no evident pattern to differences in petal size and color; these have largely been assigned to <i></i>var.<i> glandulosa</i>.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>At its most distinctive, Drymocallis glandulosa is a robust, densely glandular plant with widely branched leafy inflorescences (except var. viscida), relatively short, stout pedicels, broad sepals with rounded, mucronate tips (except var. viscida and sometimes var. reflexa) that are often significantly enlarged in fruit, and non-overlapping petals that are shorter than to scarcely equal to the sepals. The relatively large achenes are blunter and redder than those of most other species of Drymocallis, as discussed by J. Clausen et al. (1940).</p> | + | --><p>At its most distinctive, <i>Drymocallis glandulosa</i> is a robust, densely glandular plant with widely branched leafy inflorescences (except <i></i>var.<i> viscida</i>), relatively short, stout pedicels, broad sepals with rounded, mucronate tips (except <i></i>var.<i> viscida</i> and sometimes <i></i>var.<i> reflexa</i>) that are often significantly enlarged in fruit, and non-overlapping petals that are shorter than to scarcely equal to the sepals. The relatively large achenes are blunter and redder than those of most other species of <i>Drymocallis</i>, as discussed by J. Clausen et al. (1940).</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
|publication year=1898 | |publication year=1898 | ||
|special status=Selected by author to be illustrated | |special status=Selected by author to be illustrated | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/8f726806613d60c220dc4493de13607dd3150896/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V9/V9_471.xml |
|subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | |subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | ||
|tribe=Rosaceae tribe Potentilleae | |tribe=Rosaceae tribe Potentilleae | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 18 September 2019
Caudex branches short. Stems tufted, (1–)1.5–7.5 dm; base 1–5 mm diam., moderately to densely septate-glandular. Leaves sparsely to moderately hairy; basal (3–)6–30 cm, leaflet pairs (1–)2–4; terminal leaflet broadly obovate to rhombic-elliptic, (1–)1.5–7(–8) × 1–5 cm, teeth usually double (irregularly single in var. viscida), (4–)6–18(–20) per side, apex rounded to obtuse; cauline 0–3, developed or reduced, leaflet pairs 1–4. Inflorescences (2–)5–40-flowered, leafy or not, open or of congested clusters terminating branches, (1/10–)1/5–3/4 of stem, usually wide (narrow in var. viscida), branch angles (15–)20–55°. Pedicels 1–10 (proximal to 30) mm, not or sparsely short-hairy, predominantly septate-glandular. Flowers opening widely; epicalyx bractlets linear-lanceolate to elliptic, 1.5–7(–8) × 0.5–2.5(–3) mm; sepals spreading or reflexed, (3–)4–11 mm, apex usually broadly obtuse with mucronate tip, sometimes acute; petals not overlapping, spreading or reflexed, cream-white to yellow, narrowly to broadly obovate or ovate to nearly round, 2–6.5 × 1.5–5.5 mm, shorter than or equal to sepals; filaments 0.5–2 mm, anthers 0.5–1 mm; styles thickened, 1–1.5 mm. Achenes reddish brown, 0.9–1.5 mm.
Distribution
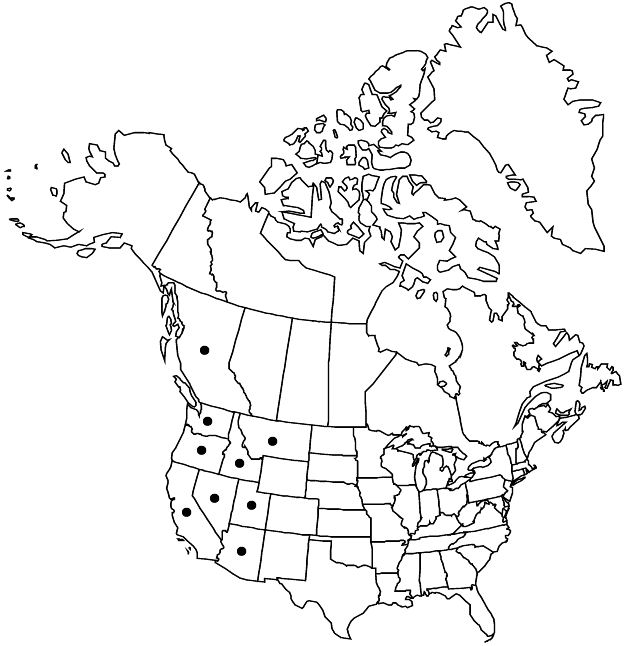
w North America, nw Mexico.
Discussion
Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).
Even with the removal of most of the subspecies of Potentilla glandulosa treated by Keck, Drymocallis glandulosa encompasses an inordinate range of variation. This is because of the apparently clinal variation between the coastal extreme (var. wrangelliana), with leafy inflorescences and broad cream-white petals, the montane var. reflexa, with less leafy inflorescences and narrow yellow petals, and the transitional interior var. glandulosa. Variety reflexa, in turn, intergrades in the mountains of southern California with var. viscida, which is anomalous in D. glandulosa with its narrow inflorescences and irregularly single-toothed leaflets. Variation outside of California is unclear, with no evident pattern to differences in petal size and color; these have largely been assigned to var. glandulosa.
At its most distinctive, Drymocallis glandulosa is a robust, densely glandular plant with widely branched leafy inflorescences (except var. viscida), relatively short, stout pedicels, broad sepals with rounded, mucronate tips (except var. viscida and sometimes var. reflexa) that are often significantly enlarged in fruit, and non-overlapping petals that are shorter than to scarcely equal to the sepals. The relatively large achenes are blunter and redder than those of most other species of Drymocallis, as discussed by J. Clausen et al. (1940).
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Petals obovate-elliptic to broadly ovate to nearly round, (2–)3.5–5.5 mm wide, cream-white to ± yellow; sepals spreading, apices obtuse to rounded; inflorescences ± to very leafy; pedicels 1–5 (proximal to 30) mm | > 2 |
| 1 | Petals narrowly ovate to narrowly obovate or obovate-elliptic, 1.5–3 mm wide, yellow; sepals reflexed, apices acute to obtuse; inflorescences ± leafy or not; pedicels 2–10 (proximal to 20) mm | > 3 |
| 2 | Petals (3–)3.5–5 mm, usually ± yellow, sometimes cream-white; inland. | Drymocallis glandulosa var. glandulosa |
| 2 | Petals (4–)4.5–6.5 mm, usually cream-white, sometimes pale yellow; ± coastal. | Drymocallis glandulosa var. wrangelliana |
| 3 | Inflorescences usually wide, branch angles (15–)25–55°; leaflet teeth usually double, rarely single. | Drymocallis glandulosa var. reflexa |
| 3 | Inflorescences narrow, branch angles 15–30(–40)°; leaflet teeth single or double. | Drymocallis glandulosa var. viscida |