Difference between revisions of "Ferocactus wislizeni"
Cact. 3: 127. 1922.
FNA>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} | }} | ||
|common_names=Compass barrel;Arizona barrel cactus;candy barrel cactus | |common_names=Compass barrel;Arizona barrel cactus;candy barrel cactus | ||
| − | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/ | + | |special_status={{Treatment/ID/Special_status |
| + | |code=F | ||
| + | |label=Illustrated | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/Basionym | ||
|name=Echinocactus wislizeni | |name=Echinocactus wislizeni | ||
|authority=Engelmann | |authority=Engelmann | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/ | + | |rank=species |
| + | |publication_title=in F. A. Wislizenus, Mem. Tour N. Mexico, | ||
| + | |publication_place=96. 1848 | ||
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Basionym | ||
|name=Echinocactus emoryi | |name=Echinocactus emoryi | ||
|authority=Engelmann 1848 | |authority=Engelmann 1848 | ||
| + | |rank=species | ||
| + | |publication_title= | ||
| + | |publication_place= | ||
}} | }} | ||
|synonyms= | |synonyms= | ||
| Line 23: | Line 33: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Stems </b>usually leaning southward in adulthood, depressed-spheric to ovoid-cylindric, 19–100(–300) × (20–)36–65(–100) cm. <b>Ribs</b> 20–30(–40), shallowly notched immediately above each areole. <b>Spines</b> 16–25(–29) per areole, central spines and larger radial spines dull pink, gray, or tan; smallest spines per areole white, slender, often bristlelike, less than 1 mm diam., strongly contrasting with central spines; central spines (1–)2–4, often with several, subulate subcentral spines, rigid; principal central spine strongly hooked (very rarely straight), 36–120(–150) mm from curve of hook to base of spine, 1.5–4(–7) mm wide, strongly annulate, terete, ± angular, or flattened and often adaxially troughlike; other central spines subulate, slightly smaller. <b>Flowers</b> similar in color inside and out, 4–8.5 × 4–6.5 cm; inner tepals orange, red, or yellow with orange to red midstripes, or wholly yellow; stigma lobes yellow, orange, or red. <b>Fruits</b> ± readily dehiscent through basal pore, bright yellow, 35–60 × 18–40 mm, thick walled, leathery or fleshy, locule dry, hollow except for seeds. <b>Seeds</b> (1.9–)2–2.5(–2.9) mm, essentially smooth with very narrow and slightly raised reticulations. <b>2n</b> = 22.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering late summer(-fall). | ||
|habitat=Desert scrub, grasslands, south-facing slopes in lower edges of oak woodlands, flats, bajadas, mountainsides, usually relatively deep soils of limestone and igneous origin | |habitat=Desert scrub, grasslands, south-facing slopes in lower edges of oak woodlands, flats, bajadas, mountainsides, usually relatively deep soils of limestone and igneous origin | ||
|elevation=100-1600(-1800) m | |elevation=100-1600(-1800) m | ||
|distribution=Ariz.;N.Mex.;Tex.;Mexico (Chihuahua;Sonora). | |distribution=Ariz.;N.Mex.;Tex.;Mexico (Chihuahua;Sonora). | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>The stems of Ferocactus wislizeni commonly lean southward, hence the vernacular name, compass barrel. Eventually they fall to the ground from their own weight, uprooting themselves.</p><!-- | + | |discussion=<p>The stems of <i>Ferocactus wislizeni</i> commonly lean southward, hence the vernacular name, compass barrel. Eventually they fall to the ground from their own weight, uprooting themselves.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Introgressive hybridization with Ferocactus cylindraceus is thus far not documented, but is often invoked as an explanation for difficulty in identifying individual specimens in or near the wide region of sympatry. The putative hybrids mostly vanish with sufficient expertise in identifying the “parental” species.</p><!-- | + | --><p>Introgressive hybridization with <i>Ferocactus cylindraceus</i> is thus far not documented, but is often invoked as an explanation for difficulty in identifying individual specimens in or near the wide region of sympatry. The putative hybrids mostly vanish with sufficient expertise in identifying the “parental” species.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Ferocactus wislizeni barely extends into Mexico, where two allopatric species, F. tiburonensis (G. E. Lindsay) Backeberg and F. herrerae J. G. Ortega, often are cited as varieties of F. wislizeni. All reports of intermediates with F. herrerae are based on normal F. herrerae, the subtropical species (R. S. Felger 2000).</p><!-- | + | --><p><i>Ferocactus wislizeni</i> barely extends into Mexico, where two allopatric species, F. tiburonensis (G. E. Lindsay) Backeberg and F. herrerae J. G. Ortega, often are cited as varieties of <i>F. wislizeni</i>. All reports of intermediates with F. herrerae are based on normal F. herrerae, the subtropical species (R. S. Felger 2000).</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>The finely reticulate seed coat of Ferocactus wislizeni is diagnostic among the species of Ferocactus in the flora.</p> | + | --><p>The finely reticulate seed coat of <i>Ferocactus wislizeni</i> is diagnostic among the species of <i>Ferocactus</i> in the flora.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 41: | Line 52: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Ferocactus wislizeni | name=Ferocactus wislizeni | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(Engelmann) Britton & Rose | |authority=(Engelmann) Britton & Rose | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
| Line 48: | Line 58: | ||
|basionyms=Echinocactus wislizeni;Echinocactus emoryi | |basionyms=Echinocactus wislizeni;Echinocactus emoryi | ||
|family=Cactaceae | |family=Cactaceae | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering late summer(-fall). | ||
|habitat=Desert scrub, grasslands, south-facing slopes in lower edges of oak woodlands, flats, bajadas, mountainsides, usually relatively deep soils of limestone and igneous origin | |habitat=Desert scrub, grasslands, south-facing slopes in lower edges of oak woodlands, flats, bajadas, mountainsides, usually relatively deep soils of limestone and igneous origin | ||
|elevation=100-1600(-1800) m | |elevation=100-1600(-1800) m | ||
| Line 54: | Line 65: | ||
|publication title=Cact. | |publication title=Cact. | ||
|publication year=1922 | |publication year=1922 | ||
| − | |special status= | + | |special status=Illustrated |
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V4/V4_445.xml |
|subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | |subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | ||
|genus=Ferocactus | |genus=Ferocactus | ||
|species=Ferocactus wislizeni | |species=Ferocactus wislizeni | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Ferocactus]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Ferocactus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:58, 5 November 2020
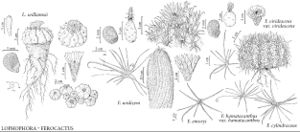
Stems usually leaning southward in adulthood, depressed-spheric to ovoid-cylindric, 19–100(–300) × (20–)36–65(–100) cm. Ribs 20–30(–40), shallowly notched immediately above each areole. Spines 16–25(–29) per areole, central spines and larger radial spines dull pink, gray, or tan; smallest spines per areole white, slender, often bristlelike, less than 1 mm diam., strongly contrasting with central spines; central spines (1–)2–4, often with several, subulate subcentral spines, rigid; principal central spine strongly hooked (very rarely straight), 36–120(–150) mm from curve of hook to base of spine, 1.5–4(–7) mm wide, strongly annulate, terete, ± angular, or flattened and often adaxially troughlike; other central spines subulate, slightly smaller. Flowers similar in color inside and out, 4–8.5 × 4–6.5 cm; inner tepals orange, red, or yellow with orange to red midstripes, or wholly yellow; stigma lobes yellow, orange, or red. Fruits ± readily dehiscent through basal pore, bright yellow, 35–60 × 18–40 mm, thick walled, leathery or fleshy, locule dry, hollow except for seeds. Seeds (1.9–)2–2.5(–2.9) mm, essentially smooth with very narrow and slightly raised reticulations. 2n = 22.
Phenology: Flowering late summer(-fall).
Habitat: Desert scrub, grasslands, south-facing slopes in lower edges of oak woodlands, flats, bajadas, mountainsides, usually relatively deep soils of limestone and igneous origin
Elevation: 100-1600(-1800) m
Distribution
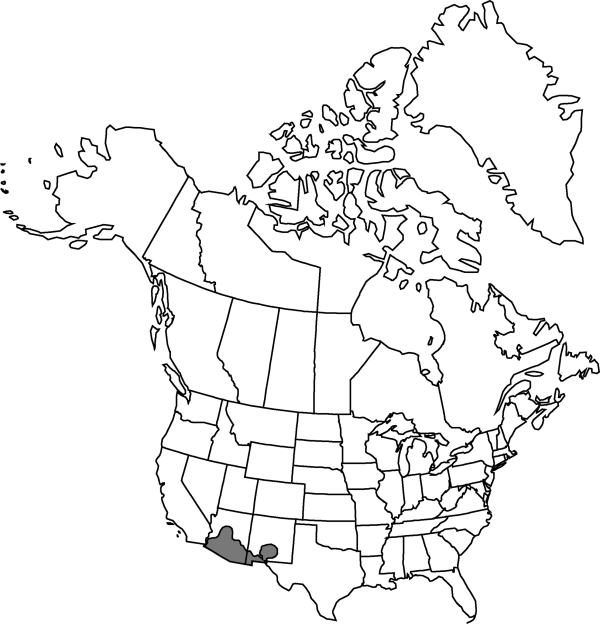
Ariz., N.Mex., Tex., Mexico (Chihuahua, Sonora).
Discussion
The stems of Ferocactus wislizeni commonly lean southward, hence the vernacular name, compass barrel. Eventually they fall to the ground from their own weight, uprooting themselves.
Introgressive hybridization with Ferocactus cylindraceus is thus far not documented, but is often invoked as an explanation for difficulty in identifying individual specimens in or near the wide region of sympatry. The putative hybrids mostly vanish with sufficient expertise in identifying the “parental” species.
Ferocactus wislizeni barely extends into Mexico, where two allopatric species, F. tiburonensis (G. E. Lindsay) Backeberg and F. herrerae J. G. Ortega, often are cited as varieties of F. wislizeni. All reports of intermediates with F. herrerae are based on normal F. herrerae, the subtropical species (R. S. Felger 2000).
The finely reticulate seed coat of Ferocactus wislizeni is diagnostic among the species of Ferocactus in the flora.
Selected References
None.