Difference between revisions of "Hesperevax acaulis"
Fl. Francisc., 402. 1897.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
|distribution=sw United States. | |distribution=sw United States. | ||
|discussion=<p>Varieties 3 (3 in the flora).</p><!-- | |discussion=<p>Varieties 3 (3 in the flora).</p><!-- | ||
| − | --><p>The varieties of Hesperevax acaulis show enough geographic and ecologic segregation correlated with morphologic differences to warrant taxonomic recognition. Across west-central California, where all three are broadly sympatric, the varieties tend to occur in different habitats and/or elevation zones. Intermediate specimens are difficult to assign with confidence.</p> | + | --><p>The varieties of <i>Hesperevax acaulis</i> show enough geographic and ecologic segregation correlated with morphologic differences to warrant taxonomic recognition. Across west-central California, where all three are broadly sympatric, the varieties tend to occur in different habitats and/or elevation zones. Intermediate specimens are difficult to assign with confidence.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
|publication year=1897 | |publication year=1897 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/8f726806613d60c220dc4493de13607dd3150896/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V19-20-21/V19_783.xml |
|tribe=Asteraceae tribe Gnaphalieae | |tribe=Asteraceae tribe Gnaphalieae | ||
|genus=Hesperevax | |genus=Hesperevax | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 18 September 2019
Plants 0.5–7 cm. Stems 0 or 1–10, erect to prostrate; branches usually 0, sometimes proximal and/or distal. Leaves basal or cauline, sessile or petiolate, distal congested, larger than proximal (if present), largest 4–22(–32) × 0.5–4(–5) mm; petioles: lengths 0–1.5 times blade lengths, bases scarcely thickened, pliant to somewhat cartilaginous; capitular leaves 6–12 (rarely more) per glomerule or head, whorled, ± erect or distally spreading, unlike pistillate paleae. Heads terminal, borne singly or, rarely, in dense glomerules (3–7 mm diam.) of 2–8 mixed with leaves and, rarely, some borne singly in axils (then smaller), campanulate, 2–4 × 1.5–3.5 mm, heights 1–1.5 times diams. Receptacles distinct, 0.9–1.9 × 0.8–1.7 mm. Pistillate paleae in 2–5 series, spirally ranked, broadly spatulate, 1–3 mm. Staminate paleae surpassing pistillate, 1.6–3.2 mm, lengths 0.6–0.8 times head heights; apices spreading. Functionally staminate florets 2–5(–12); corollas 0.6–1 mm. Cypselae 0.6–1.6 mm.
Distribution
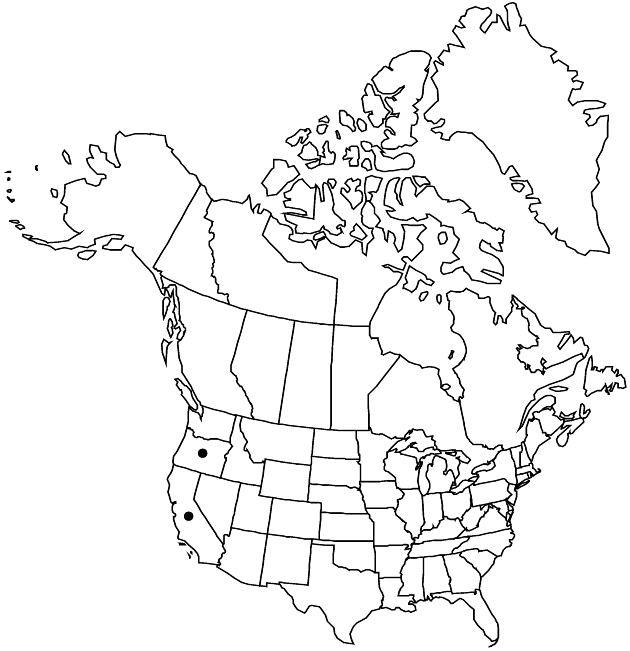
sw United States.
Discussion
Varieties 3 (3 in the flora).
The varieties of Hesperevax acaulis show enough geographic and ecologic segregation correlated with morphologic differences to warrant taxonomic recognition. Across west-central California, where all three are broadly sympatric, the varieties tend to occur in different habitats and/or elevation zones. Intermediate specimens are difficult to assign with confidence.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Stems ± erect; largest leaves (9–)12–22(–32) × 2–4 mm; longest staminate paleae 2.5–3.2 mm | Hesperevax acaulis var. robustior |
| 1 | Stems usually ± prostrate or 0; largest leaves mostly 4–12 × 0.5–2 mm; longest staminate paleae 1.6–2.4 mm | > 2 |
| 2 | Leaves petiolate, largest mostly 4–7 × 1–2 mm, blades ± round, obtuse | Hesperevax acaulis var. ambusticola |
| 2 | Leaves sessile or obscurely petiolate, largest mostly 7–12 × 0.5–2 mm, blades oblanceolate, acute | Hesperevax acaulis var. acaulis |