Difference between revisions of "Leymus simplex var. luxurians"
Treatment appears in FNA Volume 24. Treatment on page 359.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Leymus simplex var. luxurians grows at a few locations in Wyoming. It sometimes grows close to var. simplex. It may represent clones that have access to more water and/or more nutrients, but the absence of intermediate plants suggests a genetic distinction.</p> | + | |discussion=<p><i>Leymus simplex </i>var.<i> luxurians</i> grows at a few locations in Wyoming. It sometimes grows close to <i></i>var.<i> simplex</i>. It may represent clones that have access to more water and/or more nutrients, but the absence of intermediate plants suggests a genetic distinction.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Leymus simplex var. luxurians | name=Leymus simplex var. luxurians | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(Scribn. & T.A. Williams) Beetle | |authority=(Scribn. & T.A. Williams) Beetle | ||
|rank=variety | |rank=variety | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
|publication year= | |publication year= | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/f50eec43f223ca0e34566be0b046453a0960e173/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V24/V24_514.xml |
|subfamily=Poaceae subfam. Pooideae | |subfamily=Poaceae subfam. Pooideae | ||
|tribe=Poaceae tribe Triticeae | |tribe=Poaceae tribe Triticeae | ||
Revision as of 21:22, 16 December 2019
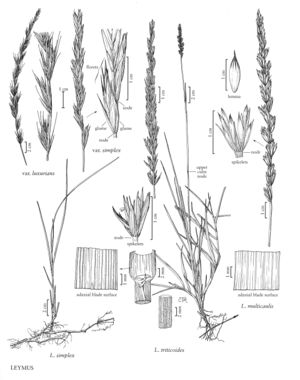
Culms 55-75 cm tall, 2-2.5 mm thick. Spikes 10-27 cm long; internodes 10-20 mm. Spikelets 20-25 mm, with 6-12 florets.
Discussion
Leymus simplex var. luxurians grows at a few locations in Wyoming. It sometimes grows close to var. simplex. It may represent clones that have access to more water and/or more nutrients, but the absence of intermediate plants suggests a genetic distinction.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
None.
... more about "Leymus simplex var. luxurians"