Difference between revisions of "Quercus engelmannii"
Ill. W. Amer. Oaks 1: 33, plate 17. 1889.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Trees,</b> subevergreen, to 10 m. <b>Bark</b> gray or whitish, closely furrowed. <b>Twigs</b> light brown, 1-1.5 mm diam., densely or sparsely stellate-tomentose, soon glabrate. <b>Buds</b> reddish brown, subspheric to broadly ovoid, 1-2 mm, glabrous or basal scales pubescent; stipules persistent about terminal buds. <b>Leaves</b>: petiole (2-)3-4(-6) mm. <b>Leaf</b> blade oblong to elliptic, occasionally lanceolate or ovate, (20-)30-60(-80) × (5-)10-20(-25) mm, base cuneate to cordate, margins entire, undulate, sometimes irregularly toothed, especially toward apex, secondary veins 7-8(-10) on each side, branched, apex acute or broadly rounded; surfaces abaxially blue-green or pale green, densely and loosely glandular-tomentose, quickly glabrate or persistently floccose, especially about base of midrib, at maturity strongly glaucous, adaxially gray-green or pale green, bluish green or glaucous. <b>Acorns</b> solitary or paired, subsessile or on peduncle to 5-6 mm; cup cup-shaped or shallowly cup-shaped, 8-10 mm deep × 10-15 mm wide, enclosing 1/3 nut, scales 1.5-3 mm wide, strongly and regularly tuberculate near base of cup, gray-pubescent; nut light brown, ovoid or oblong, 15-25 × 12-14 mm, glabrate or puberulent about apex. <b>Cotyledons</b> connate. <b>2n</b> = 24.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|habitat=Oak woodlands, margins of chaparral, arroyos, slopes and bajadas | |habitat=Oak woodlands, margins of chaparral, arroyos, slopes and bajadas | ||
|elevation=50-1200 m | |elevation=50-1200 m | ||
| − | |distribution=Calif.;Mexico (Baja California) | + | |distribution=Calif.;Mexico (Baja California). |
|discussion=<p>Quercus engelmannii is closely related to and possibly conspecific with Q. oblongifolia. The cups of Q. engelmannii are larger, deeper, and generally more tuberculate than those of Q. oblongifolia, and the scales are usually larger. Based on available samples, the nuts of Q. engelmannii are consistently larger than those of Q. oblongifolia, apparently with little, if any, overlap in diameter. Considerably more variation occurs within Q. engelmannii in leaf form, possibly reflecting introgression from other white oak species such as Q. cornelius-mulleri, Q. dumosa, and Q. durata (see treatment).</p><!-- | |discussion=<p>Quercus engelmannii is closely related to and possibly conspecific with Q. oblongifolia. The cups of Q. engelmannii are larger, deeper, and generally more tuberculate than those of Q. oblongifolia, and the scales are usually larger. Based on available samples, the nuts of Q. engelmannii are consistently larger than those of Q. oblongifolia, apparently with little, if any, overlap in diameter. Considerably more variation occurs within Q. engelmannii in leaf form, possibly reflecting introgression from other white oak species such as Q. cornelius-mulleri, Q. dumosa, and Q. durata (see treatment).</p><!-- | ||
--><p>On Catalina Island, Quercus engelmannii is known only from a small grove of trees. Putative hybrids between Q. engelmannii and Q. cornelius-mulleri are common in areas of contact between the two species in Riverside and San Diego counties in southern California. Such a population was the basis for Q. acutidens Torrey [Q. dumosa var. acutidens (Torrey) Wenzig]. Other names applied to those populations are Q. macdonaldii var. elegantula Greene and Q. dumosa var. elegantula (Greene) Jepson. Variable in leaf form and stature, those intermediates form extensive populations and are probably best disposed of under the name Q. ×acutidens.</p> | --><p>On Catalina Island, Quercus engelmannii is known only from a small grove of trees. Putative hybrids between Q. engelmannii and Q. cornelius-mulleri are common in areas of contact between the two species in Riverside and San Diego counties in southern California. Such a population was the basis for Q. acutidens Torrey [Q. dumosa var. acutidens (Torrey) Wenzig]. Other names applied to those populations are Q. macdonaldii var. elegantula Greene and Q. dumosa var. elegantula (Greene) Jepson. Variable in leaf form and stature, those intermediates form extensive populations and are probably best disposed of under the name Q. ×acutidens.</p> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
|habitat=Oak woodlands, margins of chaparral, arroyos, slopes and bajadas | |habitat=Oak woodlands, margins of chaparral, arroyos, slopes and bajadas | ||
|elevation=50-1200 m | |elevation=50-1200 m | ||
| − | |distribution=Calif.;Mexico (Baja California) | + | |distribution=Calif.;Mexico (Baja California). |
|reference=None | |reference=None | ||
|publication title=Ill. W. Amer. Oaks | |publication title=Ill. W. Amer. Oaks | ||
|publication year=1889 | |publication year=1889 | ||
|special status=Selected by author to be illustrated | |special status=Selected by author to be illustrated | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna- | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/9216fc802291cd3df363fd52122300479582ede7/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V3/V3_542.xml |
|genus=Quercus | |genus=Quercus | ||
|section=Quercus sect. Quercus | |section=Quercus sect. Quercus | ||
|species=Quercus engelmannii | |species=Quercus engelmannii | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Quercus sect. Quercus]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Quercus sect. Quercus]] | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 27 July 2019
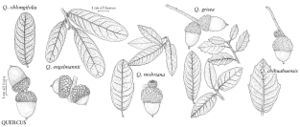
Trees, subevergreen, to 10 m. Bark gray or whitish, closely furrowed. Twigs light brown, 1-1.5 mm diam., densely or sparsely stellate-tomentose, soon glabrate. Buds reddish brown, subspheric to broadly ovoid, 1-2 mm, glabrous or basal scales pubescent; stipules persistent about terminal buds. Leaves: petiole (2-)3-4(-6) mm. Leaf blade oblong to elliptic, occasionally lanceolate or ovate, (20-)30-60(-80) × (5-)10-20(-25) mm, base cuneate to cordate, margins entire, undulate, sometimes irregularly toothed, especially toward apex, secondary veins 7-8(-10) on each side, branched, apex acute or broadly rounded; surfaces abaxially blue-green or pale green, densely and loosely glandular-tomentose, quickly glabrate or persistently floccose, especially about base of midrib, at maturity strongly glaucous, adaxially gray-green or pale green, bluish green or glaucous. Acorns solitary or paired, subsessile or on peduncle to 5-6 mm; cup cup-shaped or shallowly cup-shaped, 8-10 mm deep × 10-15 mm wide, enclosing 1/3 nut, scales 1.5-3 mm wide, strongly and regularly tuberculate near base of cup, gray-pubescent; nut light brown, ovoid or oblong, 15-25 × 12-14 mm, glabrate or puberulent about apex. Cotyledons connate. 2n = 24.
Phenology: Flowering in spring.
Habitat: Oak woodlands, margins of chaparral, arroyos, slopes and bajadas
Elevation: 50-1200 m
Distribution
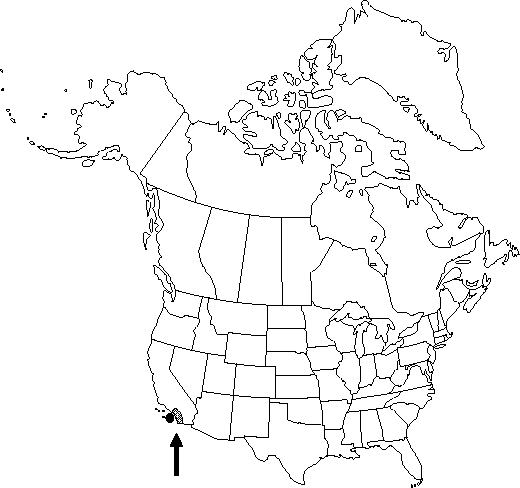
Calif., Mexico (Baja California).
Discussion
Quercus engelmannii is closely related to and possibly conspecific with Q. oblongifolia. The cups of Q. engelmannii are larger, deeper, and generally more tuberculate than those of Q. oblongifolia, and the scales are usually larger. Based on available samples, the nuts of Q. engelmannii are consistently larger than those of Q. oblongifolia, apparently with little, if any, overlap in diameter. Considerably more variation occurs within Q. engelmannii in leaf form, possibly reflecting introgression from other white oak species such as Q. cornelius-mulleri, Q. dumosa, and Q. durata (see treatment).
On Catalina Island, Quercus engelmannii is known only from a small grove of trees. Putative hybrids between Q. engelmannii and Q. cornelius-mulleri are common in areas of contact between the two species in Riverside and San Diego counties in southern California. Such a population was the basis for Q. acutidens Torrey [Q. dumosa var. acutidens (Torrey) Wenzig]. Other names applied to those populations are Q. macdonaldii var. elegantula Greene and Q. dumosa var. elegantula (Greene) Jepson. Variable in leaf form and stature, those intermediates form extensive populations and are probably best disposed of under the name Q. ×acutidens.
Selected References
None.