Difference between revisions of "Rosa mollis"
in J. E. Smith et al., Engl. Bot. 35: plate 2459. 1812.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
|publication year=1812 | |publication year=1812 | ||
|special status=Introduced | |special status=Introduced | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/f6b125a955440c0872999024f038d74684f65921/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V9/V9_138.xml |
|subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | |subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | ||
|tribe=Rosaceae tribe Roseae | |tribe=Rosaceae tribe Roseae | ||
Revision as of 21:35, 24 September 2019
Shrubs, forming large thickets; rhizomatous. Stems usually spreading and arching, erect, 8–15(–20) dm; distal branches erect or spreading, bark reddish when exposed, pruinose when young or shaded; infrastipular prickles paired, erect, 5–6 × 3–4 mm, lengths ± uniform, internodal prickles similar or smaller, mixed with aciculi. Leaves deciduous, 8–11(–14) cm; stipules 15–20 × 5–10 mm, auricles 5–8 mm, margins glabrous or ciliate, surfaces usually puberulent to tomentulose, sometimes glabrous, eglandular; petiole and rachis without pricklets, pubescent, eglandular; leaflets (5–)7, glands resin-scented when crushed, terminal: petiolule 10–17 mm, blade elliptic to ovate, 12–35 × 10–18 mm, base cuneate, sometimes rounded, margins 1–2-serrate, teeth 14–18 per side, apex acute, sometimes rounded, abaxial surfaces tomentose, resinous-glandular, sometimes eglandular, adaxial light green, dull, glabrous or mostly tomentulose. Inflorescences panicles, 1 or 2(–5)-flowered. Pedicels erect or slightly reflexed, (5–)15–35 mm, sparingly stipitate-glandular or eglandular; bracts (1–)2, ovate-lanceolate, 10–12 × 4–5 mm, margins irregularly glandular-serrate, surfaces glabrous or pubescent, eglandular. Flowers 3–4.5 cm diam.; hypanthium globose, 5–7 × 5–7 mm, stipitate-glandular or setose, neck absent; sepals spreading, ovate-lanceolate, 20–25 × (4–)5 mm, margins entire, tip 8–10 × 0.5–1 mm, abaxially densely glandular or stipitate-glandular; petals deep pink, rarely white, 9–16 × 10–16 mm; carpels 50–65, styles lanate, exsert 1.5 mm beyond stylar orifice (3.5 mm diam.) of hypanthial disc (5 mm diam.). Hips red to purplish, globose to depressed-globose, 11–16 × 12–15(–20) mm, glabrous, sometimes setose, stipitate-glandular; sepals persistent, erect. Achenes 60, dark tan to black, 4–5 × 1.5–2 mm. 2n = 28, 35, 42.
Phenology: Flowering Jun–Jul.
Habitat: Thickets, stream banks, roadsides, overgrown pastures
Elevation: 300–400 m
Distribution
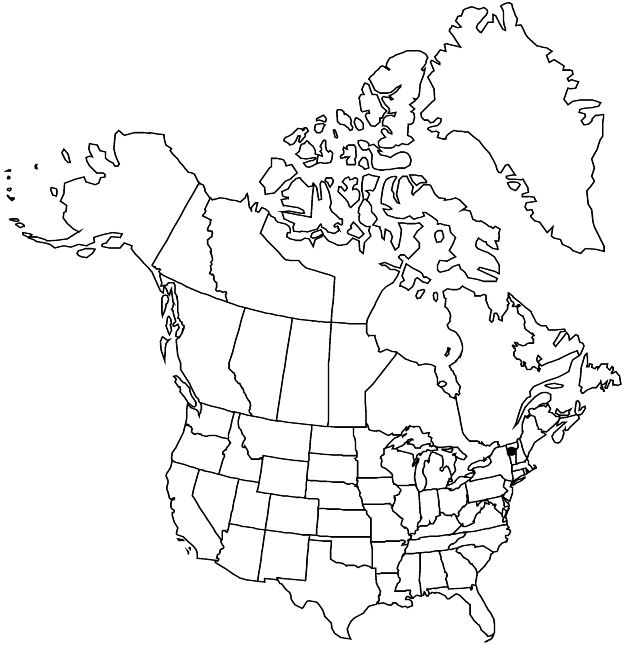
Vt., n, c Europe.
Discussion
Rosa mollis is introduced from Scotland.
Rosa mollis is closely allied to R. villosa Linnaeus; the two were treated as distinct by W. J. Bean (1970–1988) and A. V. Gilman (2012).
Selected References
None.