Difference between revisions of "Rudbeckia hirta"
Sp. Pl. 2: 907. 1753.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|distribution=e North America. | |distribution=e North America. | ||
|discussion=<p>Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).</p><!-- | |discussion=<p>Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).</p><!-- | ||
| − | --><p>Some strains of Rudbeckia hirta are cultivated and/or used in seed mixes for “re-naturalization” and erosion control.</p> | + | --><p>Some strains of <i>Rudbeckia hirta</i> are cultivated and/or used in seed mixes for “re-naturalization” and erosion control.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
|publication year=1753 | |publication year=1753 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/8f726806613d60c220dc4493de13607dd3150896/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V19-20-21/V21_122.xml |
|tribe=Asteraceae tribe Heliantheae | |tribe=Asteraceae tribe Heliantheae | ||
|subtribe=Asteraceae (tribe Heliantheae) subtribe Rudbeckiinae | |subtribe=Asteraceae (tribe Heliantheae) subtribe Rudbeckiinae | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 18 September 2019
Annuals, biennials, or perennials, to 100 cm (taprooted or roots fibrous). Stems hispid to hirsute (hairs spreading, 1+ mm). Leaves: blades elliptic, lanceolate, or ovate (not lobed), bases attenuate to cuneate, margins entire or serrate, apices acute, faces hispid to hirsute; basal petiolate, blades 8–30 × 0.5–7 cm; cauline petiolate or sessile, blades (sometimes pandurate) 3–20 × 0.4–4 cm. Heads borne singly or (2–5) in loose, corymbiform arrays. Phyllaries to 3 cm (faces hispid to hirsute). Receptacles hemispheric to ovoid; paleae 4–6 mm, apices acute, often attenuate, abaxial tips hirsute to hispid. Ray florets 8–16; laminae (usually uniformly yellow to yellow-orange or with a basal maroon splotch, sometimes mostly maroon) elliptic to oblong or oblanceolate, 15–45 × 5–10 mm, abaxially hispid to hirsute. Discs 12–22 × 10–20 mm. Disc florets 250–500+; corollas proximally yellowish green, distally brown-purple, 3–4.2 mm; style branches ca. 1.5 mm, apices subulate. Cypselae 1.5–2.7 mm; pappi 0.
Distribution
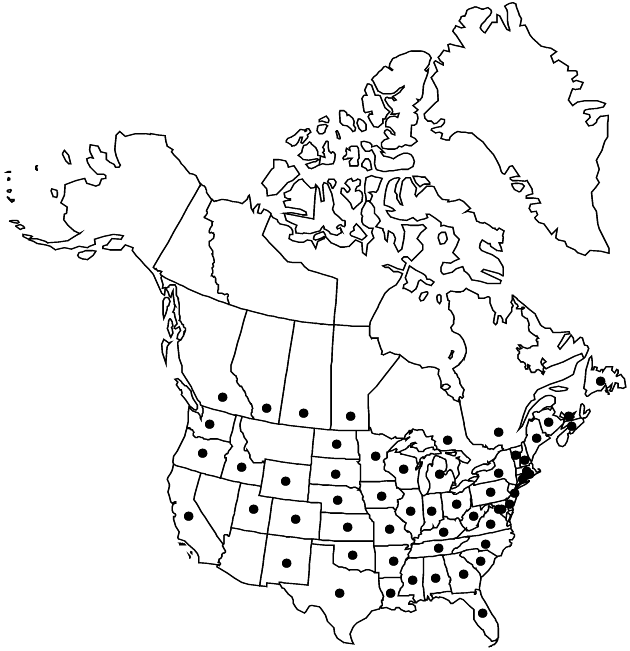
e North America.
Discussion
Varieties 4 (4 in the flora).
Some strains of Rudbeckia hirta are cultivated and/or used in seed mixes for “re-naturalization” and erosion control.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Annuals, biennials, or perennials; stems branched at bases or proximal to or at or near mid heights, leafy mostly toward bases (leaves smaller distally); peduncles usually at least 1/2 plant heights (Gulf Coastal Plain, Florida to Texas) | > 2 |
| 1 | Biennials or perennials; stems branched mostly beyond mid heights, leafy ± throughout; peduncles to 1/3 plant heights | > 3 |
| 2 | Stems branched mostly at or near mid heights; basal leaves oblanceolate, faces hispid to ± sericeous; Georgia to Texas | Rudbeckia hirta var. angustifolia |
| 2 | Stems branched at or near bases (plants often scapiform); basal leaves obovate to nearly orbiculate, faces scabrous to hirsute; c, s Florida | Rudbeckia hirta var. floridana |
| 3 | Leaves: basal blades broadly ovate to broadly elliptic, 2.5–7 cm wide (lengths mostly 2 times widths), margins coarsely toothed; cauline (sometimes sessile) lanceolate, ovate, or pandurate (mostly Appalachian Highlands toIllinois) | Rudbeckia hirta var. hirta |
| 3 | Leaves: basal blades lanceolate to oblanceolate, 1–2.5(–5) cm wide (lengths 3–5 times widths), margins entire or serrulate; cauline blades spatulate, oblanceolate, or broadly linear | Rudbeckia hirta var. pulcherrima |