Difference between revisions of "Anemone acutiloba"
Proc. & Trans. Roy. Soc. Canada 2(4): 30. 1884.
FNA>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
}}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | }}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | ||
|code=F | |code=F | ||
| − | |label= | + | |label=Illustrated |
}} | }} | ||
| − | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/ | + | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/Basionym |
|name=Hepatica acutiloba | |name=Hepatica acutiloba | ||
|authority=de Candolle | |authority=de Candolle | ||
| + | |rank=species | ||
| + | |publication_title=Prodr. | ||
| + | |publication_place=1: 22. 1824 | ||
}} | }} | ||
|synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | |synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Hepatica acuta | |name=Hepatica acuta | ||
|authority=(Pursh) Britton | |authority=(Pursh) Britton | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=species |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Hepatica nobilis var. acuta | |name=Hepatica nobilis var. acuta | ||
|authority=(Pursh) Steyermark | |authority=(Pursh) Steyermark | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=variety |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Hepatica triloba var. acuta | |name=Hepatica triloba var. acuta | ||
|authority=Pursh | |authority=Pursh | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=variety |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Hepatica triloba var. acutiloba | |name=Hepatica triloba var. acutiloba | ||
|authority=(de Candolle) Warner | |authority=(de Candolle) Warner | ||
| + | |rank=variety | ||
}} | }} | ||
|hierarchy=Ranunculaceae;Anemone;Anemone acutiloba | |hierarchy=Ranunculaceae;Anemone;Anemone acutiloba | ||
| Line 39: | Line 46: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
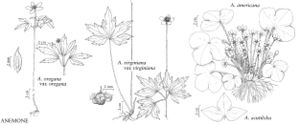
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Aerial </b>shoots 5-19 cm, from rhizomes, rhizomes ascending to horizontal. <b>Basal</b> leaves 3-15, often purplish abaxially, simple, deeply divided; petiole 3-19 cm; leaf blade widely orbiculate, 1.3-8 × 1.8- -11.5 cm, base cordate, margins entire, apex acute or acuminate, surfaces strongly villous to glabrescent; lobes 3(-5), deltate, 0.7-4 cm wide; middle lobe 70-90% of total blade length. <b>Inflorescences</b> 1-flowered, villous to pilose; involucral bracts 3, 1-tiered, simple, dissimilar to basal leaves, lanceolate to ovate, 0.53-1.8 × 0.27-0.95 cm, sessile, calyx-like, closely subtending flowers, bases distinct, cuneate, margins entire, apex acute, strongly villous to glabrescent. <b>Flowers</b>: sepals 5-12, white to pink or bluish, ovate to obovate, 6-14.6 × 2.2-5.8 mm, glabrous; petals absent; stamens 10-30. <b>Heads</b> of achenes spheric; pedicel 0.1-0.4 cm. <b>Achenes</b>: body narrowly ovoid, 3.5-4.7 × 1.3-1.9 mm, slightly winged, hispid, gradually tapering; beak indistinct. <b>2n</b>=14.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| Line 46: | Line 53: | ||
|elevation=0-1200 m | |elevation=0-1200 m | ||
|distribution=Ont.;Que.;Ala.;Ark.;Conn.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Minn.;Mo.;N.H.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Pa.;S.C.;Tenn.;Vt.;Va.;W.Va.;Wis. | |distribution=Ont.;Que.;Ala.;Ark.;Conn.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Minn.;Mo.;N.H.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Pa.;S.C.;Tenn.;Vt.;Va.;W.Va.;Wis. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>In North America, Anemone acutiloba and A. americana are sufficiently well differentiated to enable the distinction of the two species. Some intermediates do occur but it is uncertain as to whether thes intermediates or hybrids. The fact that the two species are highly sympatric and still maintain their differences implies that they should still be recognized as distinctive species (see G.L. Stebbins 1993).</p><!-- | + | |discussion=<p>In North America, <i>Anemone acutiloba</i> and <i>A. americana</i> are sufficiently well differentiated to enable the distinction of the two species. Some intermediates do occur but it is uncertain as to whether thes intermediates or hybrids. The fact that the two species are highly sympatric and still maintain their differences implies that they should still be recognized as distinctive species (see G.L. Stebbins 1993).</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>The two North American species formerly placed in Hepatica are closely allied to the Eurasian Anemone hepatica Linnaeus [=Hepatica nobilis Miller, Hepatica hepatica (Linnaeus) Karst]. Among European collections, plants approach either A. acutiloba or A. americana in leaf morphology, but some intermediates are found (J. A. Steyermark and C. S. Steyermark 1960). North American plants differ from A. hepatica in having narrower sepals, larger involucral bracts, and shorter and less pubescent scapes. Further research, including a comparative study of breeding systems, is needed to clarify the relationship between Anemone hepatica, A. acutiloba, and A. americana. Pending such work, the eastern North American hepaticas are here recognized as distinct species.</p><!-- | + | --><p>The two North American species formerly placed in Hepatica are closely allied to the Eurasian <i>Anemone</i> hepatica Linnaeus [=Hepatica nobilis Miller, Hepatica hepatica (Linnaeus) Karst]. Among European collections, plants approach either <i>A. acutiloba</i> or <i>A. americana</i> in leaf morphology, but some intermediates are found (J. A. Steyermark and C. S. Steyermark 1960). North American plants differ from A. hepatica in having narrower sepals, larger involucral bracts, and shorter and less pubescent scapes. Further research, including a comparative study of breeding systems, is needed to clarify the relationship between <i>Anemone</i> hepatica, <i>A. acutiloba</i>, and <i>A. americana</i>. Pending such work, the eastern North American hepaticas are here recognized as distinct species.</p><!-- |
--><p>D. E. Moerman (1986) lists Hepatica acutiloba as one of the plants used medicinally by Native Americans in the treatment of abdominal pains, poor digestion, and constipation, as a wash for "twisted mouth or crossed eyes," and as a gynecological aid.</p> | --><p>D. E. Moerman (1986) lists Hepatica acutiloba as one of the plants used medicinally by Native Americans in the treatment of abdominal pains, poor digestion, and constipation, as a wash for "twisted mouth or crossed eyes," and as a gynecological aid.</p> | ||
|tables= | |tables= | ||
| Line 57: | Line 64: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Anemone acutiloba | name=Anemone acutiloba | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(de Candolle) G. Lawson | |authority=(de Candolle) G. Lawson | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
| Line 71: | Line 77: | ||
|publication title=Proc. & Trans. Roy. Soc. Canada | |publication title=Proc. & Trans. Roy. Soc. Canada | ||
|publication year=1884 | |publication year=1884 | ||
| − | |special status=Endemic; | + | |special status=Endemic;Illustrated |
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V3/V3_879.xml |
|genus=Anemone | |genus=Anemone | ||
|species=Anemone acutiloba | |species=Anemone acutiloba | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Anemone]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Anemone]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:52, 5 November 2020
Aerial shoots 5-19 cm, from rhizomes, rhizomes ascending to horizontal. Basal leaves 3-15, often purplish abaxially, simple, deeply divided; petiole 3-19 cm; leaf blade widely orbiculate, 1.3-8 × 1.8- -11.5 cm, base cordate, margins entire, apex acute or acuminate, surfaces strongly villous to glabrescent; lobes 3(-5), deltate, 0.7-4 cm wide; middle lobe 70-90% of total blade length. Inflorescences 1-flowered, villous to pilose; involucral bracts 3, 1-tiered, simple, dissimilar to basal leaves, lanceolate to ovate, 0.53-1.8 × 0.27-0.95 cm, sessile, calyx-like, closely subtending flowers, bases distinct, cuneate, margins entire, apex acute, strongly villous to glabrescent. Flowers: sepals 5-12, white to pink or bluish, ovate to obovate, 6-14.6 × 2.2-5.8 mm, glabrous; petals absent; stamens 10-30. Heads of achenes spheric; pedicel 0.1-0.4 cm. Achenes: body narrowly ovoid, 3.5-4.7 × 1.3-1.9 mm, slightly winged, hispid, gradually tapering; beak indistinct. 2n=14.
Phenology: Flowering spring.
Habitat: Deciduous woods, often in calcareous soils
Elevation: 0-1200 m
Distribution
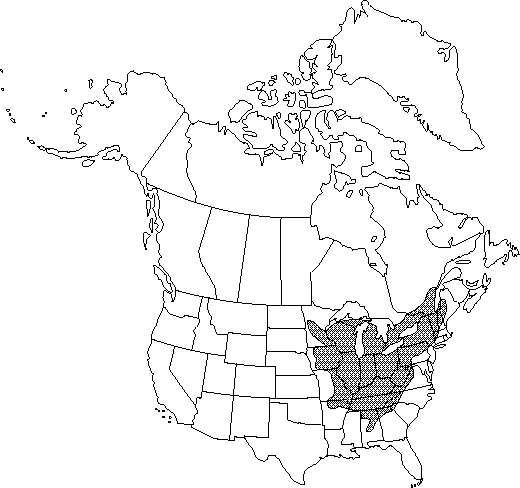
Ont., Que., Ala., Ark., Conn., Ga., Ill., Ind., Iowa, Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mo., N.H., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Pa., S.C., Tenn., Vt., Va., W.Va., Wis.
Discussion
In North America, Anemone acutiloba and A. americana are sufficiently well differentiated to enable the distinction of the two species. Some intermediates do occur but it is uncertain as to whether thes intermediates or hybrids. The fact that the two species are highly sympatric and still maintain their differences implies that they should still be recognized as distinctive species (see G.L. Stebbins 1993).
The two North American species formerly placed in Hepatica are closely allied to the Eurasian Anemone hepatica Linnaeus [=Hepatica nobilis Miller, Hepatica hepatica (Linnaeus) Karst]. Among European collections, plants approach either A. acutiloba or A. americana in leaf morphology, but some intermediates are found (J. A. Steyermark and C. S. Steyermark 1960). North American plants differ from A. hepatica in having narrower sepals, larger involucral bracts, and shorter and less pubescent scapes. Further research, including a comparative study of breeding systems, is needed to clarify the relationship between Anemone hepatica, A. acutiloba, and A. americana. Pending such work, the eastern North American hepaticas are here recognized as distinct species.
D. E. Moerman (1986) lists Hepatica acutiloba as one of the plants used medicinally by Native Americans in the treatment of abdominal pains, poor digestion, and constipation, as a wash for "twisted mouth or crossed eyes," and as a gynecological aid.
Selected References
None.