Difference between revisions of "Brachelyma subulatum"
Mém. Soc. Sci. Nat. Math. Cherbourg 28: 131. 1892.
FNA>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | }}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | ||
|code=F | |code=F | ||
| − | |label= | + | |label=Illustrated |
}} | }} | ||
| − | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/ | + | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/Basionym |
|name=Fontinalis subulata | |name=Fontinalis subulata | ||
|authority=P. Beauvois | |authority=P. Beauvois | ||
| + | |rank=species | ||
| + | |publication_title=Prodr. Aethéogam., | ||
| + | |publication_place=58. 1805 | ||
}} | }} | ||
|synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | |synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Brachelyma robustum | |name=Brachelyma robustum | ||
|authority=(Cardot) E. Britton | |authority=(Cardot) E. Britton | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=species |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Dichelyma subulatum | |name=Dichelyma subulatum | ||
|authority=(P. Beauvois) Myrin | |authority=(P. Beauvois) Myrin | ||
| + | |rank=species | ||
}} | }} | ||
|hierarchy=Fontinalaceae;Brachelyma;Brachelyma subulatum | |hierarchy=Fontinalaceae;Brachelyma;Brachelyma subulatum | ||
| Line 38: | Line 43: | ||
|elevation=low to moderate elevations (0-300 m) | |elevation=low to moderate elevations (0-300 m) | ||
|distribution=Ala.;Ark.;Fla.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Ky.;La.;Md.;Miss.;Mo.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tenn.;Tex.;Va. | |distribution=Ala.;Ark.;Fla.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Ky.;La.;Md.;Miss.;Mo.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tenn.;Tex.;Va. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Brachelyma subulatum differs from Fontinalis by its costate leaves and cucullate calyptrae. Usually the presence of costae is enough to identify B. subulatum, but costal expression in Brachelyma is sometimes variable and appears environmentally induced. It is not unusual to find plants with keeled, strongly costate proximal leaves but concave, ecostate or weakly costate apical leaves. Brachelyma subulatum has been noted as lacking an annulus; in fact it has a massive, persistent annulus similar to those in many genera of Hookeriales. Dichelyma differs from B. subulatum in having longer setae and larger calyptrae that cover the capsule and often clasp the distal seta. Brachelyma subulatum appears to be a weak segregate of Dichelyma. Brachelyma subulatum differs from many other aquatic or semi-aquatic mosses in its keeled-conduplicate leaves.</p> | + | |discussion=<p><i>Brachelyma subulatum</i> differs from <i>Fontinalis</i> by its costate leaves and cucullate calyptrae. Usually the presence of costae is enough to identify <i>B. subulatum</i>, but costal expression in <i>Brachelyma</i> is sometimes variable and appears environmentally induced. It is not unusual to find plants with keeled, strongly costate proximal leaves but concave, ecostate or weakly costate apical leaves. <i>Brachelyma subulatum</i> has been noted as lacking an annulus; in fact it has a massive, persistent annulus similar to those in many genera of Hookeriales. <i>Dichelyma</i> differs from <i>B. subulatum</i> in having longer setae and larger calyptrae that cover the capsule and often clasp the distal seta. <i>Brachelyma subulatum</i> appears to be a weak segregate of <i>Dichelyma</i>. <i>Brachelyma subulatum</i> differs from many other aquatic or semi-aquatic mosses in its keeled-conduplicate leaves.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 47: | Line 52: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Brachelyma subulatum | name=Brachelyma subulatum | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(P. Beauvois) Cardot | |authority=(P. Beauvois) Cardot | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
| Line 60: | Line 64: | ||
|publication title=Mém. Soc. Sci. Nat. Math. Cherbourg | |publication title=Mém. Soc. Sci. Nat. Math. Cherbourg | ||
|publication year=1892 | |publication year=1892 | ||
| − | |special status=Endemic; | + | |special status=Endemic;Illustrated |
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V28/V28_763.xml |
|genus=Brachelyma | |genus=Brachelyma | ||
|species=Brachelyma subulatum | |species=Brachelyma subulatum | ||
Latest revision as of 22:37, 5 November 2020
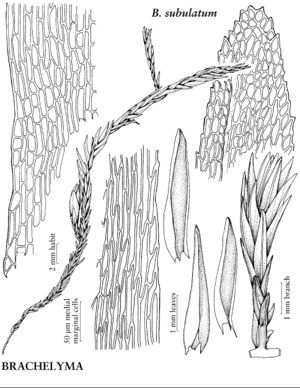
Plants green, yellowish, or brown. Stems to 30 cm; sclerodermis very thick, cortical cell walls firm; axillary hairs basal cells 1–3, subrectangular, reddish brown, distal cells 3–5, oblong, hyaline. Leaves erect to erect-spreading, imbricate, 2–4 mm; medial laminal cells 10–60 × 5–8 µm, marginal cells linear, 60–120 × 6–8 µm, forming weak border. Perigonia with leaves ecostate, antheridia few (4 or 5), paraphyses present. Perichaetia with leaves ovate-lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, 2–4 mm, margins entire, apex acute to long-acuminate, ecostate, archegonia many, paraphyses present. Seta with surface cells quadrate. Capsule 1.5–2.5 mm; annulus 8- or 9-seriate, persistent, cell walls thick; operculum 0.5–1.2 mm; exostome teeth inserted, orange or red, shorter than endostome, trabeculae widely spaced, papillose. Calyptra 2–3 mm.
Habitat: Tree trunks, branches, roots, bushes, logs, soil, rock, along rivers, flood plains and sloughs subject to inundation
Elevation: low to moderate elevations (0-300 m)
Distribution
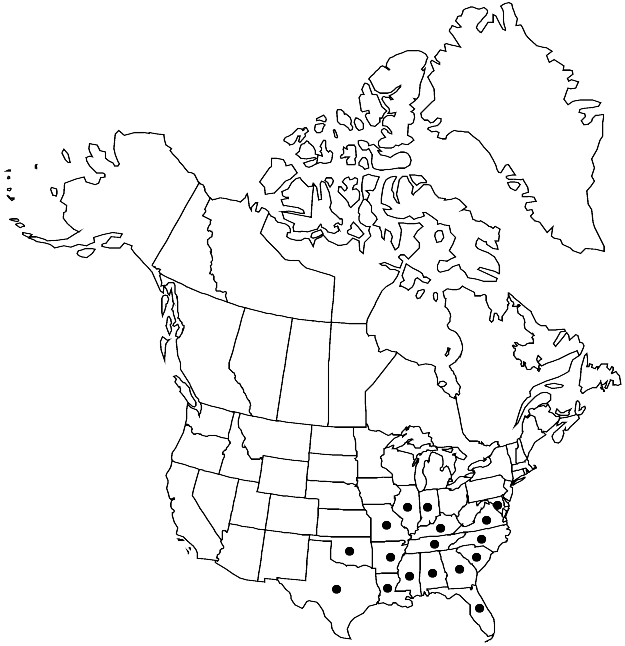
Ala., Ark., Fla., Ga., Ill., Ind., Ky., La., Md., Miss., Mo., N.C., Okla., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va.
Discussion
Brachelyma subulatum differs from Fontinalis by its costate leaves and cucullate calyptrae. Usually the presence of costae is enough to identify B. subulatum, but costal expression in Brachelyma is sometimes variable and appears environmentally induced. It is not unusual to find plants with keeled, strongly costate proximal leaves but concave, ecostate or weakly costate apical leaves. Brachelyma subulatum has been noted as lacking an annulus; in fact it has a massive, persistent annulus similar to those in many genera of Hookeriales. Dichelyma differs from B. subulatum in having longer setae and larger calyptrae that cover the capsule and often clasp the distal seta. Brachelyma subulatum appears to be a weak segregate of Dichelyma. Brachelyma subulatum differs from many other aquatic or semi-aquatic mosses in its keeled-conduplicate leaves.
Selected References
None.