Difference between revisions of "Echinocereus dasyacanthus"
in F. A. Wislizenus, Mem. Tour N. Mexico, 100. 1848.
FNA>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Treatment/ID | {{Treatment/ID | ||
|accepted_name=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | |accepted_name=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | ||
| − | |accepted_authority=Engelmann | + | |accepted_authority=Engelmann |
|publications={{Treatment/Publication | |publications={{Treatment/Publication | ||
|title=in F. A. Wislizenus, Mem. Tour N. Mexico, | |title=in F. A. Wislizenus, Mem. Tour N. Mexico, | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|name=Echinocereus pectinatus var. dasyacanthus | |name=Echinocereus pectinatus var. dasyacanthus | ||
|authority=(Engelmann) W. Earle ex N. P. Taylor | |authority=(Engelmann) W. Earle ex N. P. Taylor | ||
| + | |rank=variety | ||
}} | }} | ||
|hierarchy=Cactaceae;Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae;Echinocereus;Echinocereus dasyacanthus | |hierarchy=Cactaceae;Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae;Echinocereus;Echinocereus dasyacanthus | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Plants </b>unbranched or few branched, forming loose clumps of fewer than 20 stiff branches in old age. <b>Stems</b> erect, ovoid, becoming cylindric with age, 11–23(–40) × (4.5–)5.5–7(–10) cm; ribs (13–)15–19(–21), crests rather sharply undulate; areoles 5–11 mm apart. <b>Spines</b> 19–28 per areole, straight, appressed (radial spines) or spreading in all directions (central spines), presenting relatively bristly appearance (except when spines very short, and then having relatively smooth appearance as in <i>E. pectinatus</i>), pink to pale yellow, white, or tan, less often dark brown or purplish, annual growth increments marked (often vaguely) by rings of spines with contrasting colors; radial spines (16–)17–25(–28) per areole, 5–15(–25) mm; central spines (2–)8–12(–15) per areole, terete, largest spines 4.5–9.5(–14) mm. <b>Flowers</b> 7–8.5(–10) × 7–12 cm; flower tube 10–20 × to 10 mm; flower tube hairs 1–3 mm; inner tepals either yellow (rarely orange-yellow, sometimes becoming salmon- or rose-pink with age), or rose-pink to magenta, proximal 5–30% green in either case, (25–)32–69(–77) × 8–23 mm, tips relatively thin and delicate; anthers yellow; nectar chamber 2–6 mm. <b>Fruits</b> dark dull purplish to maroon (sometimes remaining green), 2–3.5 cm, pulp white to purplish pink. <b>2n</b> = 44.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Mar–May; fruiting Jun–Aug. | ||
|habitat=Chihuahuan desert scrub, valleys to rocky canyonsides, limestone | |habitat=Chihuahuan desert scrub, valleys to rocky canyonsides, limestone | ||
|elevation=600-1500 m | |elevation=600-1500 m | ||
|distribution=N.Mex.;Tex.;Mexico (Chihuahua;Coahuila). | |distribution=N.Mex.;Tex.;Mexico (Chihuahua;Coahuila). | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Flower color of Echinocereus dasyacanthus is spectacularly polymorphic. Unlike E. pectinatus var. wenigeri, however, the inner tepals are never white proximally. No hybrids are known to occur where the tetraploid E. dasyacanthus grows sympatrically with the diploid E. pectinatus, near the Pecos River. The names E. pectinatus var. neomexicanus and var. minor pertain to the hybrids with E. coccineus, E. ×roetteri, including E. ×lloydia. L. D. Benson (1969) misapplied the epithet neomexicanus to E. dasyacanthus. In Big Bend National Park, a few populations with unusually short spines are the basis for erroneous reports of E. pectinatus var. wenigeri, E. pectinatus var. pectinatus, and E. ctenoides (Engelmann) Lemaire. Reports from Arizona were apparently misidentifications of E. pseudopectinatus.</p> | + | |discussion=<p>Flower color of <i>Echinocereus dasyacanthus</i> is spectacularly polymorphic. Unlike <i>E. pectinatus </i>var.<i> wenigeri</i>, however, the inner tepals are never white proximally. No hybrids are known to occur where the tetraploid <i>E. dasyacanthus</i> grows sympatrically with the diploid <i>E. pectinatus</i>, near the Pecos River. The names <i>E. pectinatus</i> <i></i>var.<i> neomexicanus</i> and <i></i>var.<i> minor</i> pertain to the hybrids with <i>E. coccineus</i>, E. ×roetteri, including E. ×lloydia. L. D. Benson (1969) misapplied the epithet neomexicanus to <i>E. dasyacanthus</i>. In Big Bend National Park, a few populations with unusually short spines are the basis for erroneous reports of <i>E. pectinatus </i>var.<i> wenigeri</i>, <i>E. pectinatus</i> var. pectinatus, and E. ctenoides (Engelmann) Lemaire. Reports from Arizona were apparently misidentifications of <i>E. pseudopectinatus</i>.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | name=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | ||
| − | + | |authority=Engelmann | |
| − | |authority=Engelmann | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
|parent rank=genus | |parent rank=genus | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
|basionyms= | |basionyms= | ||
|family=Cactaceae | |family=Cactaceae | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Mar–May; fruiting Jun–Aug. | ||
|habitat=Chihuahuan desert scrub, valleys to rocky canyonsides, limestone | |habitat=Chihuahuan desert scrub, valleys to rocky canyonsides, limestone | ||
|elevation=600-1500 m | |elevation=600-1500 m | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
|publication year=1848 | |publication year=1848 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V4/V4_314.xml |
|subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | |subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | ||
|genus=Echinocereus | |genus=Echinocereus | ||
|species=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | |species=Echinocereus dasyacanthus | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Echinocereus]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Echinocereus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:57, 5 November 2020
Plants unbranched or few branched, forming loose clumps of fewer than 20 stiff branches in old age. Stems erect, ovoid, becoming cylindric with age, 11–23(–40) × (4.5–)5.5–7(–10) cm; ribs (13–)15–19(–21), crests rather sharply undulate; areoles 5–11 mm apart. Spines 19–28 per areole, straight, appressed (radial spines) or spreading in all directions (central spines), presenting relatively bristly appearance (except when spines very short, and then having relatively smooth appearance as in E. pectinatus), pink to pale yellow, white, or tan, less often dark brown or purplish, annual growth increments marked (often vaguely) by rings of spines with contrasting colors; radial spines (16–)17–25(–28) per areole, 5–15(–25) mm; central spines (2–)8–12(–15) per areole, terete, largest spines 4.5–9.5(–14) mm. Flowers 7–8.5(–10) × 7–12 cm; flower tube 10–20 × to 10 mm; flower tube hairs 1–3 mm; inner tepals either yellow (rarely orange-yellow, sometimes becoming salmon- or rose-pink with age), or rose-pink to magenta, proximal 5–30% green in either case, (25–)32–69(–77) × 8–23 mm, tips relatively thin and delicate; anthers yellow; nectar chamber 2–6 mm. Fruits dark dull purplish to maroon (sometimes remaining green), 2–3.5 cm, pulp white to purplish pink. 2n = 44.
Phenology: Flowering Mar–May; fruiting Jun–Aug.
Habitat: Chihuahuan desert scrub, valleys to rocky canyonsides, limestone
Elevation: 600-1500 m
Distribution
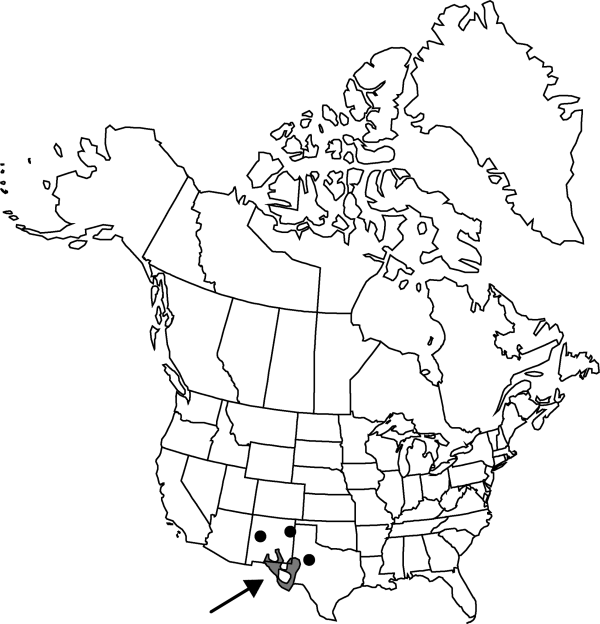
N.Mex., Tex., Mexico (Chihuahua, Coahuila).
Discussion
Flower color of Echinocereus dasyacanthus is spectacularly polymorphic. Unlike E. pectinatus var. wenigeri, however, the inner tepals are never white proximally. No hybrids are known to occur where the tetraploid E. dasyacanthus grows sympatrically with the diploid E. pectinatus, near the Pecos River. The names E. pectinatus var. neomexicanus and var. minor pertain to the hybrids with E. coccineus, E. ×roetteri, including E. ×lloydia. L. D. Benson (1969) misapplied the epithet neomexicanus to E. dasyacanthus. In Big Bend National Park, a few populations with unusually short spines are the basis for erroneous reports of E. pectinatus var. wenigeri, E. pectinatus var. pectinatus, and E. ctenoides (Engelmann) Lemaire. Reports from Arizona were apparently misidentifications of E. pseudopectinatus.
Selected References
None.