Difference between revisions of "Echinocereus fendleri"
Preis-Verz. Cact. Succ., 22. 1860.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Plants </b>unbranched or sometimes forming loose clumps of fewer than 20 somewhat flaccid branches. <b>Stems</b> erect or slightly decumbent, ovoid to cylindric with age, 7.5–17(–30) × (3.3–)3.8–7.5(–10) cm; ribs 8–11(–13), crests uninterrupted or undulate (sometimes depth of sinus between areoles is 90% of rib height in flowering plants with juvenile stem morphology); areoles (12–)15–17(–25) mm apart. <b>Spines</b> (2–)4–12(–16) per areole, straight or curved (radial spines sometimes sinuous); radial spines spreading, opaquely white, commonly with dark stripe on underside, often with contrasting black or brown spines in same areoles (rarely all brown or all white), aging gray; radial spines (2–)4–10(–12) per areole, (8–)11–39 mm; central spines (0–)1(–3) per areole, porrect or ascending, if curved, then usually directed upward, (10–)25–42(–62) mm, abaxial central spine like others in color or darker, flat to sharply angled. <b>Flowers</b> 5–11 × 5–11 cm; flower tube 10–15 × 10–30 mm; flower tube hairs 1–2 mm; inner tepals magenta [or nearly white], proximally sometimes darker or purplish maroon, 30–70 × (9.5–)12–15 mm, tips relatively thin and delicate; anthers yellow; nectar chamber (2–)3.5–6(–8) mm. <b>Fruits</b> bright red, dull carmine, or purplish maroon, less often orange-tan or purplish orange, 20–30(–50) mm, pulp magenta or red. <b>2n</b> = 22.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Apr–Jun; fruiting Jun–Aug. | ||
|habitat=Mesquite thickets, semidesert grasslands, interior chaparral, pinyon-juniper or pine-oak woodlands, limestone or igneous substrates, mostly south-facing hillsides | |habitat=Mesquite thickets, semidesert grasslands, interior chaparral, pinyon-juniper or pine-oak woodlands, limestone or igneous substrates, mostly south-facing hillsides | ||
|elevation=900-2400 m | |elevation=900-2400 m | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
|basionyms=Cereus fendleri;Echinocereus fendleri var. kuenzleri | |basionyms=Cereus fendleri;Echinocereus fendleri var. kuenzleri | ||
|family=Cactaceae | |family=Cactaceae | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Apr–Jun; fruiting Jun–Aug. | ||
|habitat=Mesquite thickets, semidesert grasslands, interior chaparral, pinyon-juniper or pine-oak woodlands, limestone or igneous substrates, mostly south-facing hillsides | |habitat=Mesquite thickets, semidesert grasslands, interior chaparral, pinyon-juniper or pine-oak woodlands, limestone or igneous substrates, mostly south-facing hillsides | ||
|elevation=900-2400 m | |elevation=900-2400 m | ||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
|publication year=1860 | |publication year=1860 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna- | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/9216fc802291cd3df363fd52122300479582ede7/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V4/V4_315.xml |
|subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | |subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | ||
|genus=Echinocereus | |genus=Echinocereus | ||
|species=Echinocereus fendleri | |species=Echinocereus fendleri | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Echinocereus]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Echinocereus]] | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 27 July 2019
Plants unbranched or sometimes forming loose clumps of fewer than 20 somewhat flaccid branches. Stems erect or slightly decumbent, ovoid to cylindric with age, 7.5–17(–30) × (3.3–)3.8–7.5(–10) cm; ribs 8–11(–13), crests uninterrupted or undulate (sometimes depth of sinus between areoles is 90% of rib height in flowering plants with juvenile stem morphology); areoles (12–)15–17(–25) mm apart. Spines (2–)4–12(–16) per areole, straight or curved (radial spines sometimes sinuous); radial spines spreading, opaquely white, commonly with dark stripe on underside, often with contrasting black or brown spines in same areoles (rarely all brown or all white), aging gray; radial spines (2–)4–10(–12) per areole, (8–)11–39 mm; central spines (0–)1(–3) per areole, porrect or ascending, if curved, then usually directed upward, (10–)25–42(–62) mm, abaxial central spine like others in color or darker, flat to sharply angled. Flowers 5–11 × 5–11 cm; flower tube 10–15 × 10–30 mm; flower tube hairs 1–2 mm; inner tepals magenta [or nearly white], proximally sometimes darker or purplish maroon, 30–70 × (9.5–)12–15 mm, tips relatively thin and delicate; anthers yellow; nectar chamber (2–)3.5–6(–8) mm. Fruits bright red, dull carmine, or purplish maroon, less often orange-tan or purplish orange, 20–30(–50) mm, pulp magenta or red. 2n = 22.
Phenology: Flowering Apr–Jun; fruiting Jun–Aug.
Habitat: Mesquite thickets, semidesert grasslands, interior chaparral, pinyon-juniper or pine-oak woodlands, limestone or igneous substrates, mostly south-facing hillsides
Elevation: 900-2400 m
Distribution
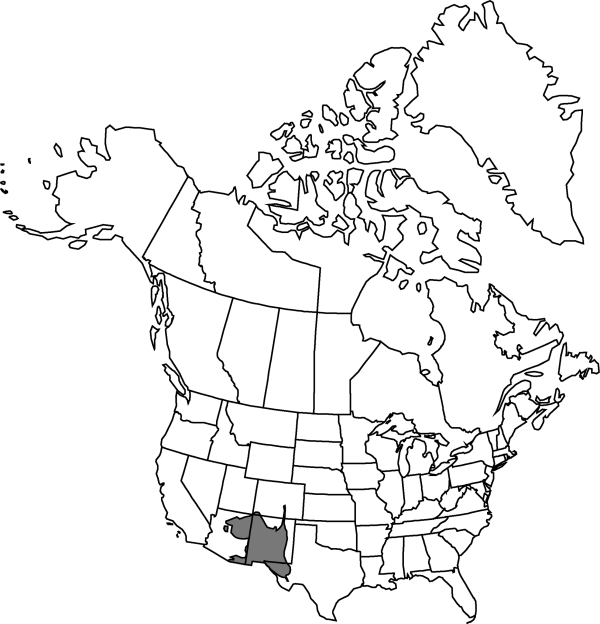
Ariz., Colo., N.Mex., Tex., Mexico (Chihuahua, Sonora).
Discussion
Frequently, some or all spines in each areole of Echinocereus fendleri are opaquely white, especially the lowermost (largest) radial spine, which is frequently strongly flattened (dorsiventrally compressed, its margins expanded and textured spongy or corky). On some immature plants, all the spines are modified in that way, reminiscent of spines of Pediocactus peeblesianus (Croizat) L. D. Benson.
Echinocereus fendleri has an indefinite number of (mostly) unnamed geographic races. One of these, var. rectispinus, of southeastern Arizona has enjoyed undeserved emphasis in the literature; it is often based on misidentifications of tetraploid E. fasciculatus.
The tuberculate stems and sparse, strangely modified spines of immature plants are retained to some extent in adulthood in some populations of Echinocereus fendleri var. fendleri. Such plants superficially resemble Pediocactus peeblesianaus. The name E. fendleri var. kuenzleri (Castetter, P. Pierce & K. H. Schwerin) L. D. Benson and its Mexican counterpart, E. hempelii Fobe, are based mainly on the stem feature. Immature plants of all populations share that distinctive appearance, strikingly different from immature plants of similar or related species, such as E. fasciculatus. In adulthood this convenient diagnostic characteristic is usually lost, rendering identification more difficult. On the Mexican border immature plants in some populations have as few as four spines per areole; they probably are intermediates with the obviously conspecific Chihuahuan taxon, E. hempelii Fobe.
Selected References
None.
