Difference between revisions of "Nymphaea mexicana"
Abh. Math.-Phys. Cl. Königl. Bayer. Akad. Wiss. 1: 365. 1832.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
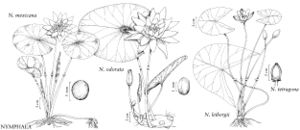
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Rhizomes </b>unbranched, erect, cylindric; stolons elongate, spongy, developing clusters of curved, fleshy, overwintering roots resembling tiny bananas at terminal nodes. <b>Leaves</b>: petiole glabrous. <b>Leaf</b> blade abaxially purplish with dark flecks, adaxially green, often with brown mottling, ovate to elliptic or nearly orbiculate, 7-18(-27) × 7-14(-18) cm, margins entire or sinuate; venation radiate and impressed centrally, without weblike pattern, principal veins 11-22; surfaces glabrous. <b>Flowers</b> floating or emersed, 6-11 cm diam., opening and closing diurnally, only sepals and outermost petals in distinct whorls of 4; sepals uniformly yellowish green, often red-tinted, evidently veined, lines of insertion on receptacle often slightly prominent; petals 12-30, yellow; stamens ca. 50-60, yellow, connective appendage minute or absent; filaments widest below middle, longer than anthers; pistil 7-10-locular, appendages at margin of stigmatic disk oblong-tapered, to 4.5 mm. <b>Seeds</b> globose, ca. 5 × 5 mm, uniformly covered with hairlike papillae 100-220 µm. <b>2n</b> = 56.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
|habitat=Outer coastal plain in alkaline lakes, ponds, warm springs, pools in marshes, sloughs, sluggish streams, ditches, and canals | |habitat=Outer coastal plain in alkaline lakes, ponds, warm springs, pools in marshes, sloughs, sluggish streams, ditches, and canals | ||
|elevation=0-1100 m | |elevation=0-1100 m | ||
| − | |distribution=Ala.;Ariz.;Calif.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tex.;ne;c Mexico | + | |distribution=Ala.;Ariz.;Calif.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tex.;ne;c Mexico. |
|discussion=<p>Nymphaea mexicana is probably introduced in most inland sites and in California, where it is considered a problematic weed in waterways; it is not common in most states except Florida. The distribution of this species is similar to that of the winter distribution of canvasback ducks, for which the bananalike tubers are an important food (J. E. Cely 1979). This species forms natural hybrids with N. odorata; the hybrids have been named N. ×thiona D. B. Ward (D. B. Ward 1977). Except for stem characteristics, which resemble one or the other parent, and their added vigor, the hybrids are generally intermediate in morphology. They are completely sterile; however, hybrids with the stolon-bearing habit of N. mexicana can form extensive clones and, although somewhat larger in stature than N. mexicana, they closely resemble that less agressive parent and could easily be mistaken for it. Some of the introductions, such as in southeastern Nevada and north-central Kentucky, are clearly this hybrid.</p> | |discussion=<p>Nymphaea mexicana is probably introduced in most inland sites and in California, where it is considered a problematic weed in waterways; it is not common in most states except Florida. The distribution of this species is similar to that of the winter distribution of canvasback ducks, for which the bananalike tubers are an important food (J. E. Cely 1979). This species forms natural hybrids with N. odorata; the hybrids have been named N. ×thiona D. B. Ward (D. B. Ward 1977). Except for stem characteristics, which resemble one or the other parent, and their added vigor, the hybrids are generally intermediate in morphology. They are completely sterile; however, hybrids with the stolon-bearing habit of N. mexicana can form extensive clones and, although somewhat larger in stature than N. mexicana, they closely resemble that less agressive parent and could easily be mistaken for it. Some of the introductions, such as in southeastern Nevada and north-central Kentucky, are clearly this hybrid.</p> | ||
|tables= | |tables= | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
|habitat=Outer coastal plain in alkaline lakes, ponds, warm springs, pools in marshes, sloughs, sluggish streams, ditches, and canals | |habitat=Outer coastal plain in alkaline lakes, ponds, warm springs, pools in marshes, sloughs, sluggish streams, ditches, and canals | ||
|elevation=0-1100 m | |elevation=0-1100 m | ||
| − | |distribution=Ala.;Ariz.;Calif.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tex.;ne;c Mexico | + | |distribution=Ala.;Ariz.;Calif.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;S.C.;Tex.;ne;c Mexico. |
|reference=capperino1985a;cely1979a | |reference=capperino1985a;cely1979a | ||
|publication title=Abh. Math.-Phys. Cl. Königl. Bayer. Akad. Wiss. | |publication title=Abh. Math.-Phys. Cl. Königl. Bayer. Akad. Wiss. | ||
|publication year=1832 | |publication year=1832 | ||
|special status=Selected by author to be illustrated;Weedy | |special status=Selected by author to be illustrated;Weedy | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna- | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/9216fc802291cd3df363fd52122300479582ede7/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V3/V3_1035.xml |
|genus=Nymphaea | |genus=Nymphaea | ||
|species=Nymphaea mexicana | |species=Nymphaea mexicana | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Nymphaea]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Nymphaea]] | ||
Revision as of 14:29, 27 July 2019
Rhizomes unbranched, erect, cylindric; stolons elongate, spongy, developing clusters of curved, fleshy, overwintering roots resembling tiny bananas at terminal nodes. Leaves: petiole glabrous. Leaf blade abaxially purplish with dark flecks, adaxially green, often with brown mottling, ovate to elliptic or nearly orbiculate, 7-18(-27) × 7-14(-18) cm, margins entire or sinuate; venation radiate and impressed centrally, without weblike pattern, principal veins 11-22; surfaces glabrous. Flowers floating or emersed, 6-11 cm diam., opening and closing diurnally, only sepals and outermost petals in distinct whorls of 4; sepals uniformly yellowish green, often red-tinted, evidently veined, lines of insertion on receptacle often slightly prominent; petals 12-30, yellow; stamens ca. 50-60, yellow, connective appendage minute or absent; filaments widest below middle, longer than anthers; pistil 7-10-locular, appendages at margin of stigmatic disk oblong-tapered, to 4.5 mm. Seeds globose, ca. 5 × 5 mm, uniformly covered with hairlike papillae 100-220 µm. 2n = 56.
Phenology: Flowering spring–fall, mainly summer farther north.
Habitat: Outer coastal plain in alkaline lakes, ponds, warm springs, pools in marshes, sloughs, sluggish streams, ditches, and canals
Elevation: 0-1100 m
Distribution
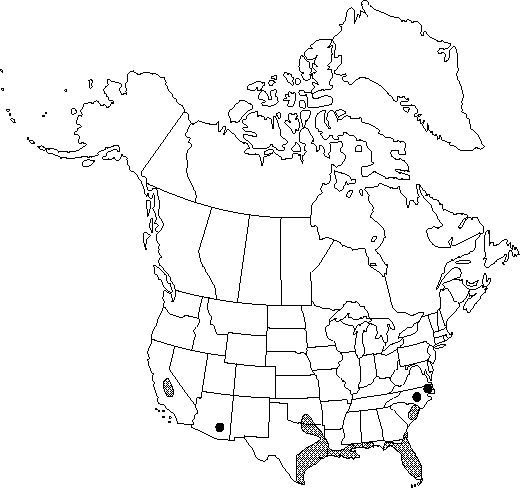
Ala., Ariz., Calif., Fla., Ga., La., Miss., N.C., Okla., S.C., Tex., ne, c Mexico.
Discussion
Nymphaea mexicana is probably introduced in most inland sites and in California, where it is considered a problematic weed in waterways; it is not common in most states except Florida. The distribution of this species is similar to that of the winter distribution of canvasback ducks, for which the bananalike tubers are an important food (J. E. Cely 1979). This species forms natural hybrids with N. odorata; the hybrids have been named N. ×thiona D. B. Ward (D. B. Ward 1977). Except for stem characteristics, which resemble one or the other parent, and their added vigor, the hybrids are generally intermediate in morphology. They are completely sterile; however, hybrids with the stolon-bearing habit of N. mexicana can form extensive clones and, although somewhat larger in stature than N. mexicana, they closely resemble that less agressive parent and could easily be mistaken for it. Some of the introductions, such as in southeastern Nevada and north-central Kentucky, are clearly this hybrid.