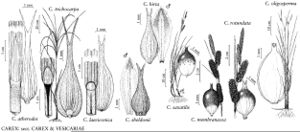
Carex saxatilis
Sp. Pl. 2: 976. 1753.
Plants usually loosely cespitose; rhizomes short, congested. Culms trigonous in cross section, 8–90 cm, scabrous distally. Leaves: basal sheaths reddish brown; ligules as wide as to slightly longer than wide; blades mid to dark green, V-shaped, sometimes with revolute margins, 0.9–6.3 mm wide, glabrous. Inflorescences 2.5–14(–20) cm; proximal bract 0.6–16(–29) cm, shorter than or equaling inflorescence; proximal 1–3 spikes pistillate, erect or the proximal often pendent; terminal 1–3 spikes staminate. Pistillate scales ovate, 1.9–4.3(–5) × 0.9–2.1 mm, as long as or shorter than perigynia, margins entire, apex obtuse or acute, awnless. Perigynia ascending, often dark-colored, obscurely few-veined, veins not running to beak, tightly investing achene, elliptic, 2.2–5.5 × 1.1–2.9 mm, apex abruptly contracted; beak 0.2–0.8 mm, bidentulate, teeth straight, to 0.3 mm. Stigmas 2. Achenes yellow, biconvex, smooth. 2n = 78, 80.
Phenology: Fruiting summer.
Habitat: Fens, bogs, wet tundra, roadside ditches, shores of lakes, ponds, and slow moving streams, often in shallow water
Elevation: 0–3700 m
Distribution
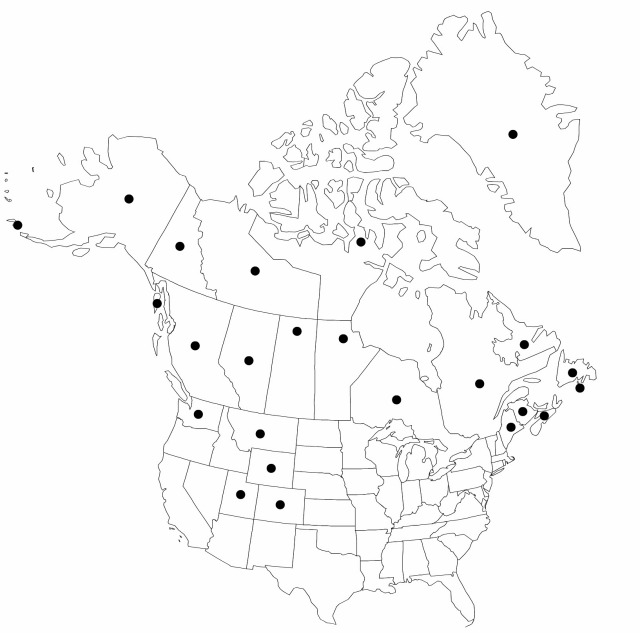
Greenland, St. Pierre and Miquelon, Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr., N.W.T., N.S., Nunavut, Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Colo., Maine, Mont., Utah, Wash., Wyo., Eurasia.
Discussion
Carex saxatilis is highly variable in North America. Plants from western North America, often named C. physocarpa, tend to be robust with long peduncles on the pistillate spikes, wide leaves, and large perigynia. These characters decrease in size eastward across North America with successively smaller plants usually referred to as C. saxatilis and C. miliaris. This weak east/west cline is confounded by large amounts of variation within small geographic areas and phenotypic plasticity. B. A. Ford et al. (1991) and B. A. Ford and P. W. Ball (1992) have demonstrated that these segregates represent elements in a continuum rather than discrete taxa.
Hybrids between Carex saxatilis and C. vesicaria (= C. ×stenolepis Lessing; = C. ×mainensis Porter ex Britton) and C. saxatilis and C. utriculata (= C. ×physocarpoides Lepage) have been found in North America (B. A. Ford et al. 1993). These hybrids are infrequent, largely sterile, and intermediate in morphology between the two parents.
Carex compacta R. Brown ex Dewey (1835, not Lamarck, 1779) is an illegitimate name that pertains here.
Selected References
None.