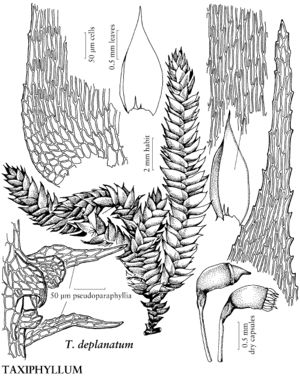
Taxiphyllum deplanatum
Musc. Buitenzorg 4: 1435. 1923.
Plants in thin to dense mats, light green to yellowish. Stems 4 cm, 1–3 mm wide, complanate-foliate; radiculose ventrally. Leaves appressed-imbricate, close, ovate to ovate-lanceolate, rarely oblong-lanceolate or oblong-ovate, symmetric to somewhat asymmetric, somewhat concave or flat, 0.9–2 × 0.4–0.8 mm; margins plane or narrowly recurved just beyond base, serrulate throughout; apex acuminate or often abruptly acute or filiform, not twisted; costa double and very short or ecostate; alar cells many, quadrate to short-rectangular, 12–27 × 9–17 µm, in 1–several rows, 3–8 cells in marginal row; laminal cells smooth; medial cells 47–136 × 7–12 µm. Seta yellowish to red, 0.7–1 cm. Capsule yellowish to light brown, oblong or ovoid, straight or arcuate, 0.8–1.5 mm; operculum 0.3–0.5 mm. Spores 11–13 µm.
Phenology: Capsules mature fall.
Habitat: Shaded siliceous or calcareous soil and rock, base of trees, exposed tree roots, rotten logs, cedar swamps
Elevation: low to high elevations (60-2700 m)
Distribution
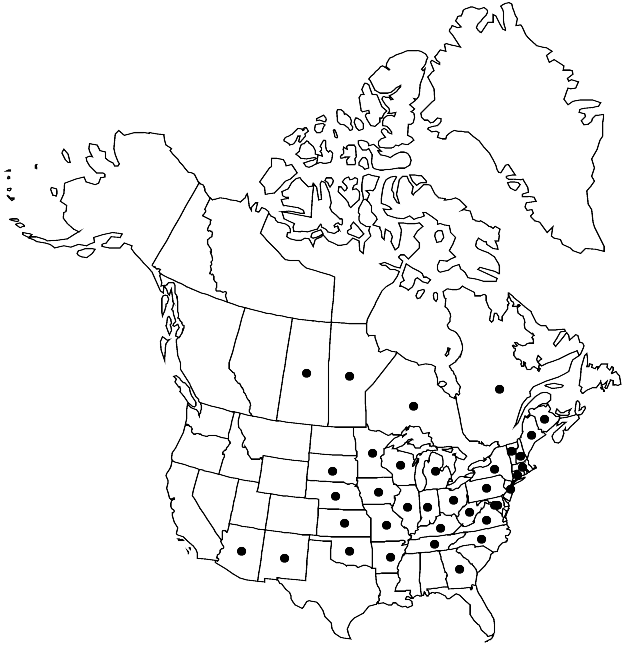
Man., N.B., Ont., Que., Sask., Ariz., Ark., Conn., D.C., Ga., Ill., Ind., Iowa, Kans., Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mo., Nebr., N.H., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Okla., Pa., S.Dak., Tenn., Vt., Va., W.Va., Wis., Mexico, Central America (Honduras).
Discussion
Taxiphyllum deplanatum is widespread in northeastern North America with disjunct populations in New Brunswick, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Arizona, and New Mexico. Taxiphyllum deplanatum has often been confused with T. taxirameum, but the two are easily distinguished superficially and microscopically. The flaccid, appressed-imbricate leaves characteristic of T. deplanatum will easily separate it from T. taxirameum with its rigid, usually distant, wide-spreading to squarrose leaves. The alar regions of T. deplanatum are well differentiated with quadrate to short-rectangular cells, 3–8 in the marginal rows, which is in striking contrast to the poorly differentiated alar regions of T. taxirameum that have only a few rectangular cells on the margins. Taxiphyllum deplanatum has been reported for the Gulf Coast region, based on a Louisiana specimen (R. R. Ireland 1969b). However, it was re-examined and found to be a misidentified specimen of T. taxirameum as W. D. Reese (1984) noted. The capsules are extremely rare.
Selected References
None.